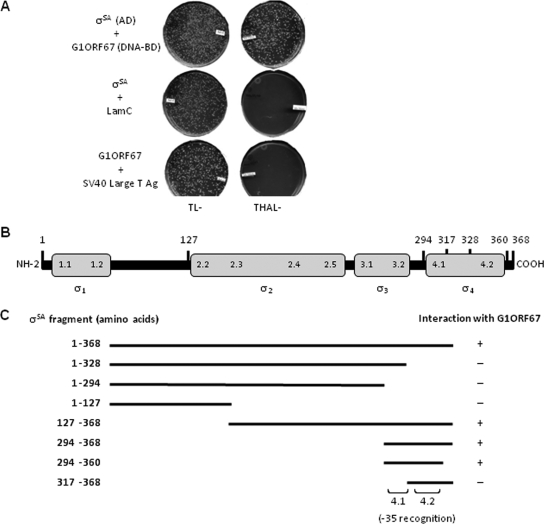
FIG. 4.
In vivo interaction of G1ORF67 with S. aureus σSA. (A) Yeast two-hybrid analysis. Constructs encoding full-length σSA (amino acids 1 to 368) as a fusion with GAL4 activation domain (AD) and G1ORF67 as a fusion with GAL4 DNA-binding domain (DNA BD) were generated and used to transform the yeast strain. Cotransformants were plated on selective medium lacking tryptophan and leucine (TL−) or lacking tryptophan, histidine, adenine, and leucine (THAL−). (B) Schematic representation of domain organization of S. aureus σSA. (C) Mapping of the minimal domain of S. aureus σSA that interacts with G1ORF67. Constructs encoding full-length σSA (amino acids 1 to 368) or its truncated derivatives were cloned as fusions with the GAL4 activation domain and used in combination with full-length G1ORF67/GAL4 DNA-binding domain in transformations. Cotransformants were plated on selective medium, and the growth or absence of growth of the yeast strain was interpreted as an interaction (+) or absence of an interaction (−), respectively, between σSA and G1ORF67.