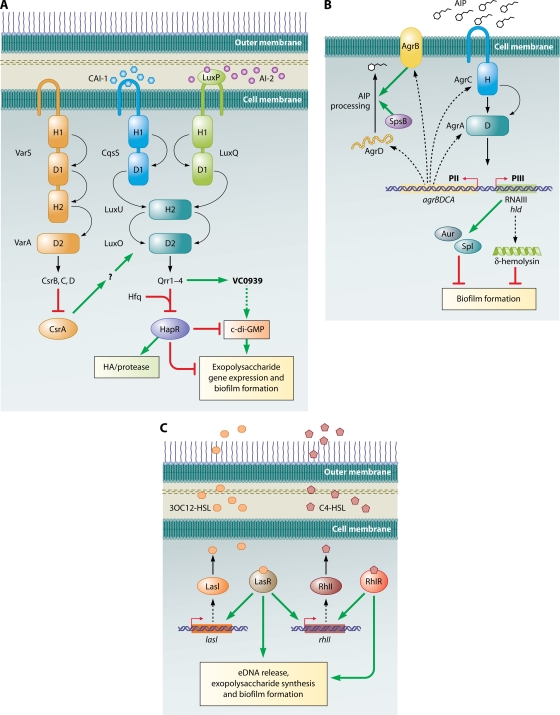
FIG. 3.
Quorum-sensing circuits and biofilm formation. (A) V. cholerae. Three quorum-sensing circuits converge on HapR to regulate biofilm formation. A HapR-independent quorum-sensing pathway involving Qrr1 to -4 and VC0939, which encodes a GGDEF family protein, has also been identified. This protein is likely to be a DGC that makes c-di-GMP, which is a positive activator of biofilm formation. HapR inhibits biofilm formation via multiple pathways, one of which is by indirectly decreasing c-di-GMP concentrations in the cell. Curved arrows denote the flow of phosphate under low-cell-density conditions. Phosphate flow is reversed at high density. H and D refer to the histidine and aspartate residues, respectively, which accept and shuttle the phosphoryl group. Dotted lines denote hypothesized effects. The question mark refers to a hypothesized intermediate effector in the pathway that has not been identified. (Adapted from reference 193 with permission of Blackwell Publishing Ltd.) (B) S. aureus: the Agr quorum-sensing pathway. A TCS composed of the histidine kinase AgrC and the response regulator AgrA responds to the presence of AIP. Phosphorylated AgrA activates transcription of the divergent PII and PIII operons. The PII operon encodes the machinery to synthesize, process, and detect AIP, while the PIII operon encodes RNAIII, the major effector of the quorum-sensing response. RNAIII regulates numerous downstream genes, two of which encode Aur and Spl proteases that are negative effectors of biofilm formation. The RNAIII transcript also encodes δ-hemolysin, which also inhibits biofilm formation. Curved arrows denote the flow of phosphate under high-cell-density conditions. H and D refer to the histidine and aspartate residues, respectively, which accept and shuttle the phosphoryl group. Broken lines connect the genes to their gene products. (C) P. aeruginosa. Las and Rhl pathways regulate quorum-sensing responses. The Rhl system is under the control of the Las system. LasR and RhlR, in the presence of their cognate autoinducers, activate a large number of genes, among which are those involved in exopolysaccharide production, eDNA, and biofilm formation. Broken lines connect the genes to their gene products.