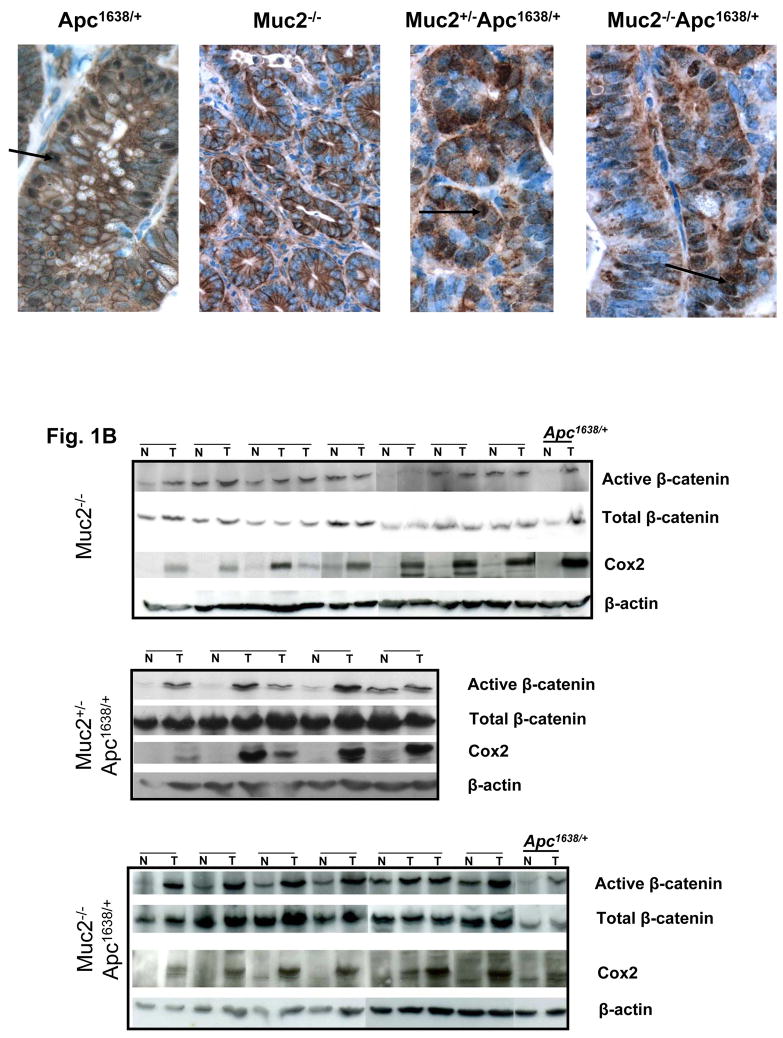
Fig. 1.
β-catenin expression in tumors of Apc1638N/+, Muc2−/− and compound double mutant Muc2−/−;Apc1638N/+ mice. Panel A shows representative immunohistochemical analysis of β-catenin expression in tumors of mice of the indicated phenotype. β-catenin nuclear localization is observed in Apc1638N/+and double mutant Muc2/Apc1638N/+ tumors (arrows), but it is not detected in Muc2−/− tumors. Total number of tumors analyzed were 3 for Apc1638N/+ and 6 for each Muc2−/− and double mutant Muc2+/−; Muc2−/−;Apc1638N/+ tumors. Panel B shows the levels of expression of activated (non-phosphorylated) and total β-catenin as well as Cox2 in cell extracts of paired normal and tumor of the indicated genotypes. β-actin levels were determined as controls for equal loading and gel transfer.