Figure 4. Inactivation properties of CaV2.2/β3 channels co-expressed with the wild-type α2δ-1 or its proteolysis mutations.
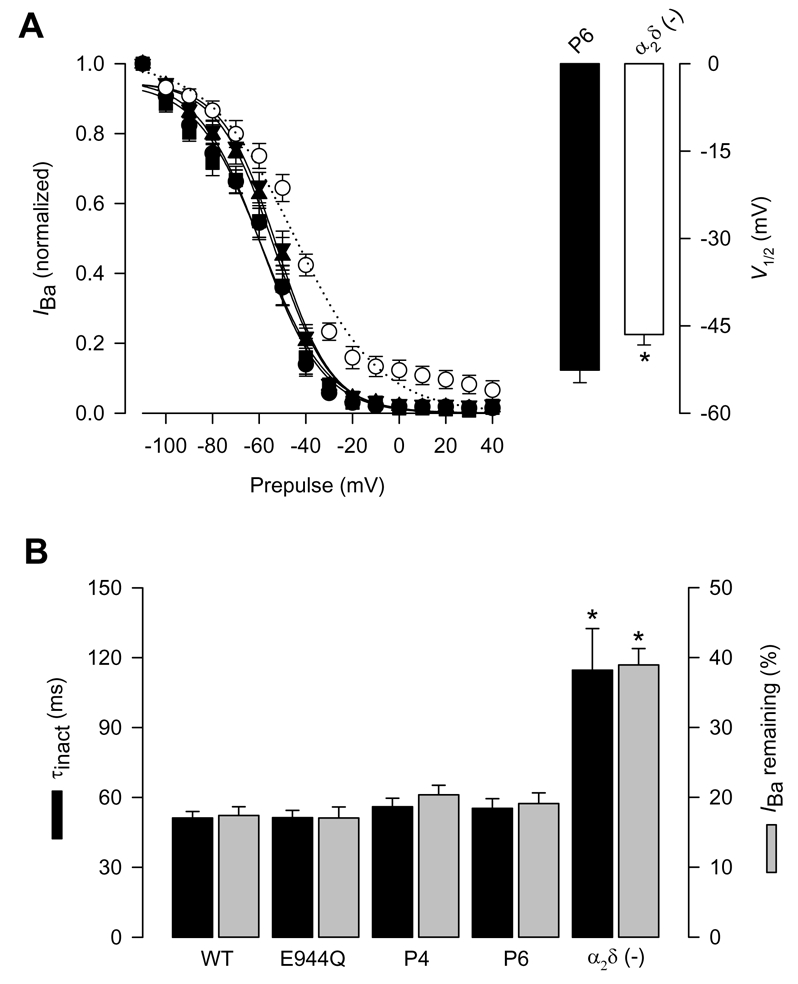
A) Left, voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation of CaV2.2/β3 channels co-expressed with wild-type CaVα2δ-1 (filled circles), its proteolysis mutants E944Q, P4 and P6 or without any α2δ subunit (open circles). Currents were recorded after conditioning pulses of 1 s duration, applied from a holding potential of −80 mV in 10 mV steps between −110 and +40 mV, followed by a 140 ms test pulse to +10 mV. The normalized data are plotted against the conditioning potentials (n = 5–11). The mean data were fitted with a Boltzmann function, the V½ values of which are given in Table 1. Right, comparison of the mean half-inactivation voltage (V1/2) for CaV2.2/β3 channels co-expressed with the P6 mutation or without the α2δ subunit. B) Average time constants of inactivation (τinact) and percentage of current remaining 140 ms into the depolarizing pulse for CaV2.2/β3 channels co-expressed with wild-type α2δ-1, its proteolysis mutants, or without any α2δ subunit (n = 11–25).
