Figure 6. The effect of VIVIT on neuronal L-type Ca2+ channels is specific to AKAP79/150.
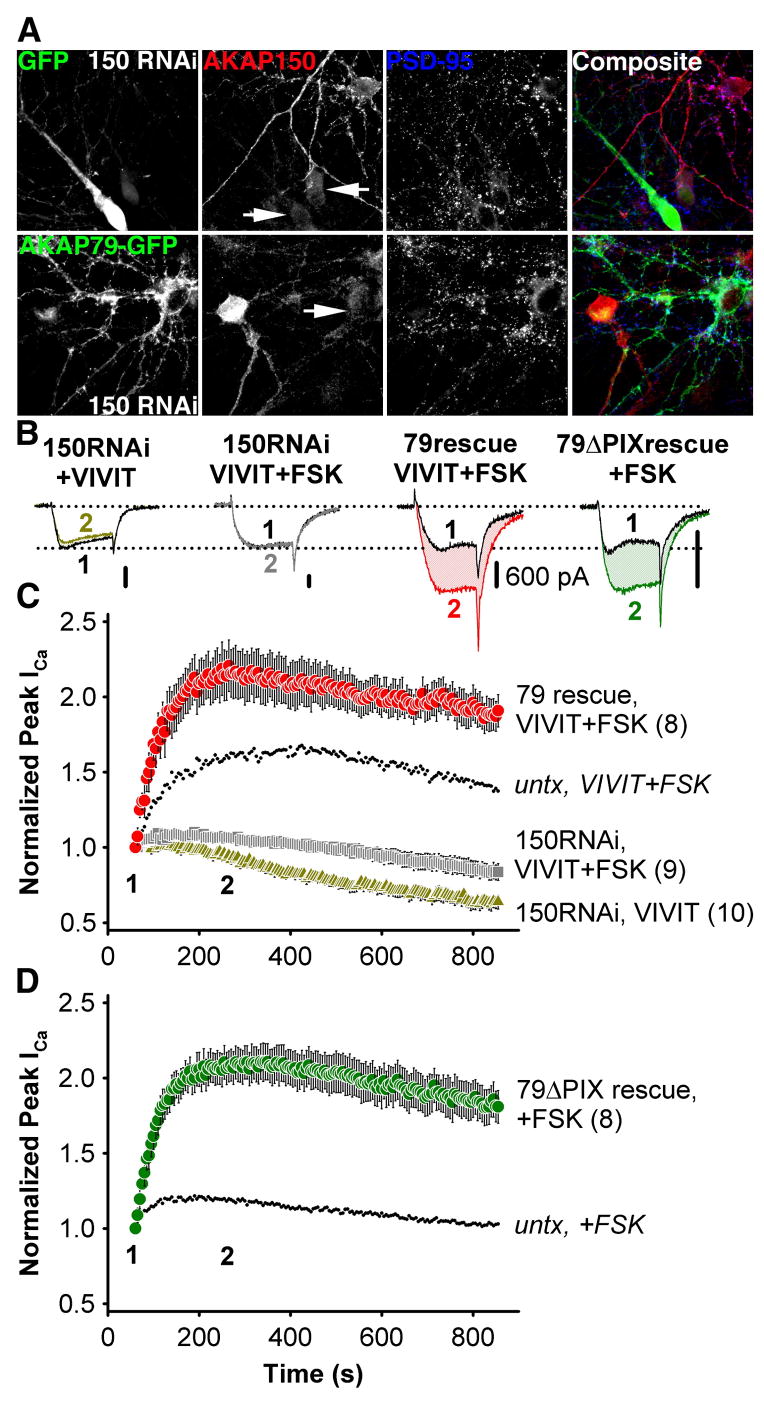
(A) Top, micrographs of primary cultured hippocampal neurons transfected with the pSilencerAKAP150-short hairpin RNAi construct (150 RNAi) and GFP, demonstrating suppression (marked with GFP and arrows) of endogenous AKAP150 (red, indirectly immunolabeled with Texas Red). Bottom, simultaneous RNAi suppression of AKAP150 expression and rescue with AKAP79-GFP in hippocampal neurons. Normal levels of AKAP150 staining are seen in adjacent untransfected neurons. PSD-95 staining (blue, indirectly immunolabeled with Alexa Fluor 647) is a postsynaptic marker of excitatory synapses.
(B) Representative current recordings 60 s (time point 1, black traces) and 250 s (time point 2, colored traces) after establishing the whole cell recording configuration for 150RNAi + VIVIT, 150RNAi + VIVIT + FSK, 79rescue + VIVIT + FSK and 79ΔPIX + FSK conditions. All scale bars indicate 600 pA.
(C) Average peak current timecourse for cells expressing 150RNAi and GFP during VIVIT dialysis (150RNAi, VIVIT,  ) or co-application of VIVIT and FSK (150RNAi, VIVIT + FSK,
) or co-application of VIVIT and FSK (150RNAi, VIVIT + FSK,  ), and for cells rescued from AKAP150 knockdown by AKAP79-GFP co-transfection (79 rescue, VIVIT + FSK,
), and for cells rescued from AKAP150 knockdown by AKAP79-GFP co-transfection (79 rescue, VIVIT + FSK,  ). Small dots reproduce the effect of VIVIT + FSK observed in untransfected neurons (
). Small dots reproduce the effect of VIVIT + FSK observed in untransfected neurons ( from Fig. 4C).
from Fig. 4C).
(D) The effect of FSK alone on neurons after AKAP150 knockdown and replacement with AKAP79ΔPIX-YFP (79ΔPIX rescue, +FSK,  ). Small dots reproduce the effect of FSK in untransfected neurons (
). Small dots reproduce the effect of FSK in untransfected neurons ( from Figure 4C).
from Figure 4C).
