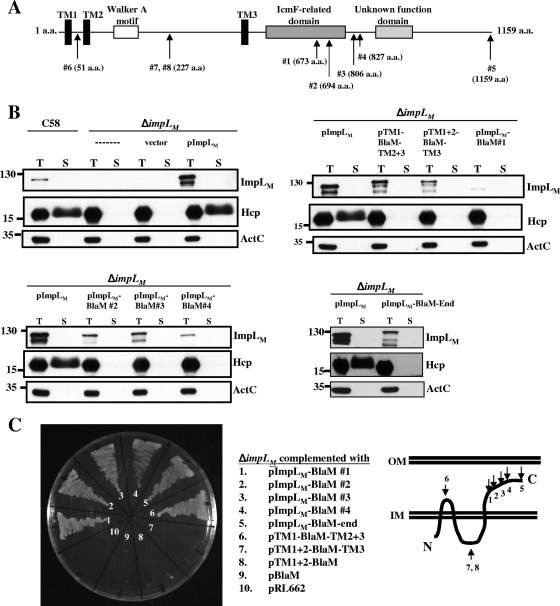
FIG. 2.
ImpLM topology analysis using β-lactamase fusions and immunoblotting of fusion proteins. (A) ImpLM domain organization predicted with the SMART software (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/). ImpLM is predicted to be an inner membrane protein with three TM domains (TM1 to TM3) (black bars) containing a Walker A motif (open bar) located between TM2 and TM3. A conserved domain with an unknown function (light gray bar) and an IcmF-related domain (dark gray bar) are located at the C terminus of ImpLM. The positions of BlaM insertions or fusions are indicated by arrows labeled with amino acid (a.a.) positions. (B) Total (T) and secreted (S) proteins isolated from wild-type, ΔimpLM, and various ImpLM-complemented strains grown in AB-MES (pH 5.5) for 6 h at 25°C were resolved by 12% glycine-SDS-PAGE. BlaM fusion proteins were analyzed to determine their expression and function in Hcp secretion by immunoblot analysis with C-ImpLM, Hcp, and ActC antibodies. The secreted proteins were collected from 1 ml of culture medium after removal of bacterial cells and were concentrated by trichloroacetic acid precipitation and analyzed as described previously (72). The nonsecreted soluble protein ActC served as an internal control. (C) A. tumefaciens ΔimpLM strains containing either the vector (pRL662) or one of the complementing plasmids containing BlaM fusions were grown in 523 medium with 250 μg/ml carbenicillin at 28°C for 24 h to examine their resistance to carbenicillin. The membrane topology of ImpLM is based on the BlaM and GFP fusion results. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated to the left of the blots. IM, inner membrane; OM, outer membrane.