FIG. 2.
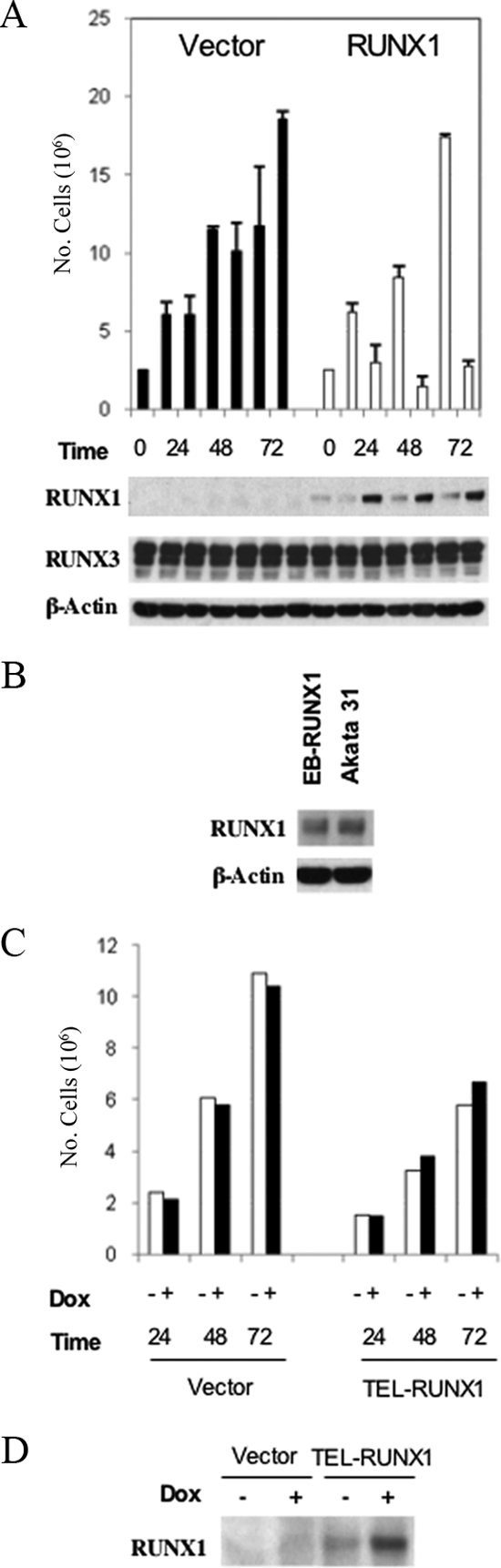
Doxycycline-inducible RUNX1c expression reduces growth in EBV-infected LCL cells. (A) IB4 LCLs were stably transfected with a doxycycline-inducible empty-vector construct (pEBtetD; filled bars) or one inducibly expressing RUNX1c (pEBtetD-RUNX1c; open bars). Cells were cultured in duplicate with and without 5 μg/ml doxycycline and were harvested at the indicated times. Cells were counted (counts are shown in the top panel as numbers of cells), and then RIPA extracts were prepared and 50 μg protein was analyzed by Western blotting for RUNX1, RUNX3, and β-actin. (B) The pEBtetD-RUNX1c cells plus doxycycline (track labeled EB-RUNX1) were coelectrophoresed at the 24-h time point with 50 μg of Akata 31 BL cell line RIPA extract, and samples were analyzed by Western blotting for RUNX1 expression. (C) IB4 LCL cells were stably transfected with empty-vector pEBtetD (vector) or doxycycline (Dox)-inducible pEBtetD-TEL-RUNX1. IB4:pEBtetD empty-vector or IB4:pEBtetD-TEL-RUNX1 cells were incubated with or without 5 μg/ml doxycycline for the indicated times and counted. (D) The IB4:pEBtetD-TEL-RUNX1 stably transfected cells or vector control cells were incubated with or without 5 μg/ml doxycycline for 24 h, and RIPA extracts were probed for TEL-RUNX1 expression.
