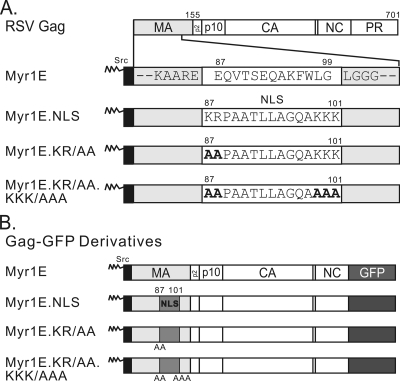
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram of RSV Gag and mutant proteins. (A) The wild-type Gag protein is depicted at the top, with cleavage products MA (light gray), p2, p10, CA, NC, and PR indicated. Amino acid numbers 155 (the end of MA) and 701 (the end of Gag) are shown above. Gag mutants from the indicated virus constructs are illustrated below, with the focus on the MA domain, which is enlarged for detail. Each mutant contains the 10-amino-acid membrane-binding domain of the v-Src protein (black box), which is myristylated (as indicated by zigzag lines). For Myr1E Gag, the downstream wild-type amino acid sequence between positions 87 and 99 (white box) is shown. Flanking residues (gray boxes) are invariable among all the mutants. The Myr1E.NLS mutant has an insertion based on the bipartite nucleoplasmin NLS sequence located between residues 87 and 101 (white box). Myr1E.KR/AA has replacements of the upstream basic residues (KR) with alanines (bold font), and Myr1E.KR/AA.KKK/AAA has both sets of critical basic residues (KR upstream and KKK downstream) in the NLS changed to alanines. (B) Gag-GFP derivatives have GFP (dark gray box) substituted for the last 7 amino acids of NC and all of PR. Amino acid changes involving the MA domain are identical to those shown above in panel A. The inserted NLS and basic residue mutations are indicated by medium-gray boxes, with the positions of alanine substitutions shown below each box.