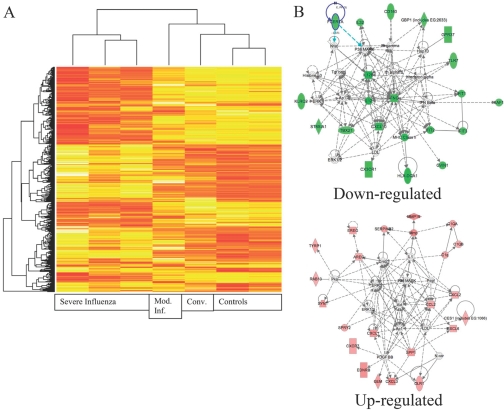
Fig. 3.
Gene expression analysis of patients with severe influenza. PBMCs were prepared at the time of plasma cytokine analysis. RNA was isolated and cRNA prepared and labeled. (A) Results from the array were clustered. Patients with severe influenza have a markedly disordered gene expression. The convalescent sample (Conv.) and the moderate influenza (Mod. Inf.) sample are much more like the controls than the severe influenza group. In evaluating the overexpressed genes, many related to potential changes in the cellular composition of the PBMCs. (B) Using network analysis, the major affected pathways for up-regulated genes are ERK, p38, Akt, AP-1, NF-κB, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. The major affected pathways for down-regulated genes are IFN-γ, IL-12, IFN-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeat 2 (IFIT2), and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A. FCERIA, FcεRIα; GBP1, guanylate-binding protein 1; Hsp70, heat shock protein 70; GPR37, G protein-coupled receptor 37; KLRC2, killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 2; IFNG, IFN-γ; XAF1, X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein-associated factor 1; ST8SIA1, ST8 α-N-acetyl-neuraminide α-2,8-sialyltransferase 1; TBX21, T-box 21; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; GVIN1, GTPase, very large IFN-inducible 1 protein; MMP19, matrix metalloproteinase 19; EREG, epiregulin; SERPINB2, serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (OVA), member 2; C1QA, complement 1 QA; AREG, amphiregulin; RAB13, member RAS oncogene family; Pka, protein kinase A; Pdgf, platelet-derived growth factor; SYN1, Synapsin I; CES1, carboxylesterase 1; SPRY2, sprouty homolog 2; SPP1, secreted phosphoprotein 1; N-cor, nuclear receptor corepressor; EDNRB, endothelin receptor type B; GEM, glycolipid-enriched membrane; OLR1, oxidized LDL (lectin-like) receptor 1.