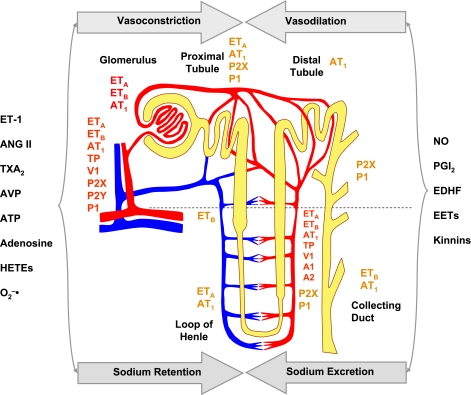
Fig. 6.
Differential distribution of receptors and mediators in the renal vasculature and nephron. Renal vascular receptors (shown in red) are activated by VCs to regulate RBF in afferent and efferent arterioles and vasa recta. VDs prevent excessive renal vasoconstriction. Decreased VDs and increased VCs lead to renal vasoconstriction and HTN. Receptors in tubules, loop of Henle, and collecting ducts (shown in brown) are modulated by substances that promote sodium retention or excretion and thereby maintain water and electrolyte balance, plasma volume, and BP. Increased sodium and water retention lead to increased plasma volume and HTN. AVP, arginine-vasopressin.