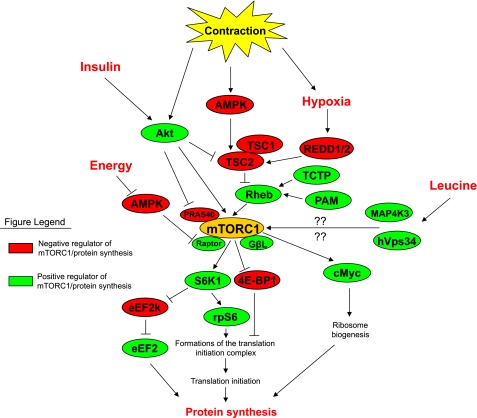
Fig. 1.
A simplified schematic representation of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling pathway driven by muscle contraction, insulin, essential amino acids (leucine), and/or energy. Proteins have been labeled to designate them as a positive (green) or negative (red) regulators of mTORC1 and muscle protein synthesis. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; Akt, protein kinase B; TSC1, tuberous sclerosis complex 1; TSC2, tuberous sclerosis complex 2; REDD1/2, regulated in development and DNA damage responses; Rheb, Ras-homologue enriched in brain; TCTP, translationally controlled tumor protein; PAM, protein associated with Myc; Raptor, regulatory associated protein of mTOR; GβL, G protein β-subunit-like protein; MAP4K3, mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase-3; hVps34, human vacuolar protein sorting-34; S6K1, p70 ribosomal S6 kinase 1; 4E-BP1, 4E binding protein 1; eEF2k, eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase; eEF2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2; rpS6, ribosomal protein S6; PRAS40, proline-rich Akt substrate-40.