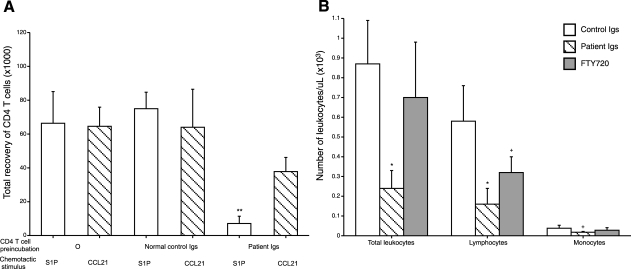
Figure 4.
Effects of patient MAW anti-lymphocyte Abs on in vivo tissue chemotaxis and blood concentrations of CD4 T cells in C57BL/6 mice. Five days prior to introduction of lymphocytes with anti-lymphocyte Abs, mice were irradiated with 600 rad. A) Inhibition of S1P-evoked chemotaxis of mouse CD4 T cells into a dorsal subcutaneous air pocket by preincubation with patient MAW Igs, but not normal Igs. Each mouse received 2.5–3.0 × 106 CD4 T cells together with either 5 mg of patient Igs or 5 mg of normal Igs intravenously in 150 μl of PBS, followed in 10 min by 0.2 ml of 10−5 M S1P or CCL21 into the air pocket. Bars and brackets depict means ± sd of results of 3–5 studies analyzed after 24 h. **P < 0.001; 1-tailed 2-sample t test. B) Suppression of mouse blood lymphocyte level by FTY720 and patient MAW Igs, but not normal control Igs. Bars and brackets represent means ± sd; 6 mice/group. Previously irradiated mice received 3.0 × 106 CD4 T cells together with either 5 mg of patient Igs, 5 mg of normal Igs, or 20 μg/kg of FTY720 intravenously in 150 μl of PBS 24 h prior to blood counts. +P < 0.05, *P < 0.01; 2-tailed 2-sample t test.