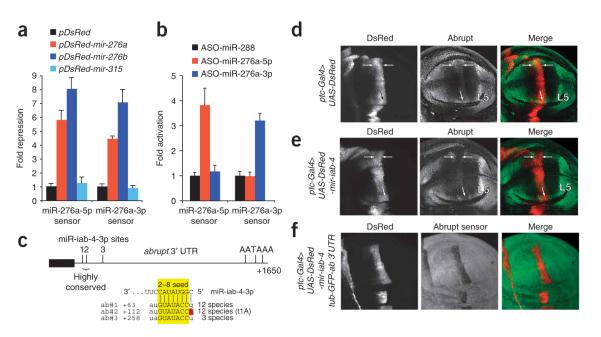
Figure 6.
Endogenous relevance of miRNA*-mediated repression. (a) Ectopic mir-276a and mir-276b, but not DsRed or mir-315, specifically repress both miR-276a-5p and miR-276a-3p sensors. The experimental design is the same as for Figure 4a; mean values and s.d. are shown. (b) 2′O-methylated antisense oligos (ASO) against endogenous miR-276a-5p and miR-276a-3p specifically derepress cognate sensors. Data were collected and analyzed as in a. (c) Abrupt is an endogenous target of the miRNA* species, miR-iab-4-3p. Of three ‘2–8’ seed matches (highlighted yellow) near the start of the abrupt 3′ UTRs (denoted ab#1, ab#2 and ab#3) two are highly conserved among divergent Drosophilids and one has a t1A feature (red). (d) Endogenous Abrupt protein in a wing pouch carrying one copy of ptc-Gal4 and two copies of UAS-DsRed. Abrupt accumulates to a high level in the L5 wing vein primordium and a lower level in the L3 vein domain (arrows). (e) Wing pouch of an animal carrying two copies of ptc-Gal4 and one copy of UAS-DsRed-mir-iab-4. Abrupt protein is reduced in L3 (arrows). Genotypes d and e express roughly equivalent amounts of DsRed and control for the neutral effect of DsRed on Abrupt. (f) In ptc-Gal4, UAS-DsRed-mir-iab-4; tub-GFP-abrupt 3′ UTR wing imaginal discs, GFP is strongly suppressed in DsRed/miR+ cells.