Figure 2.
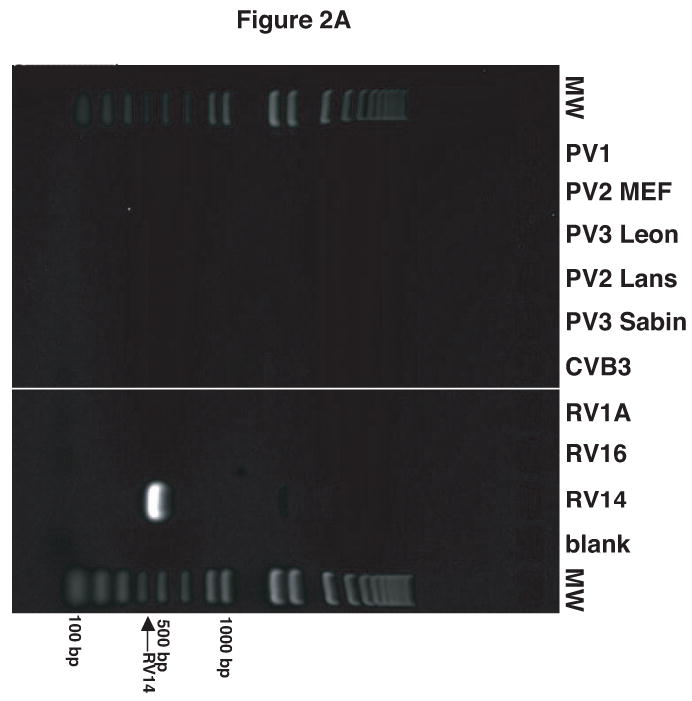
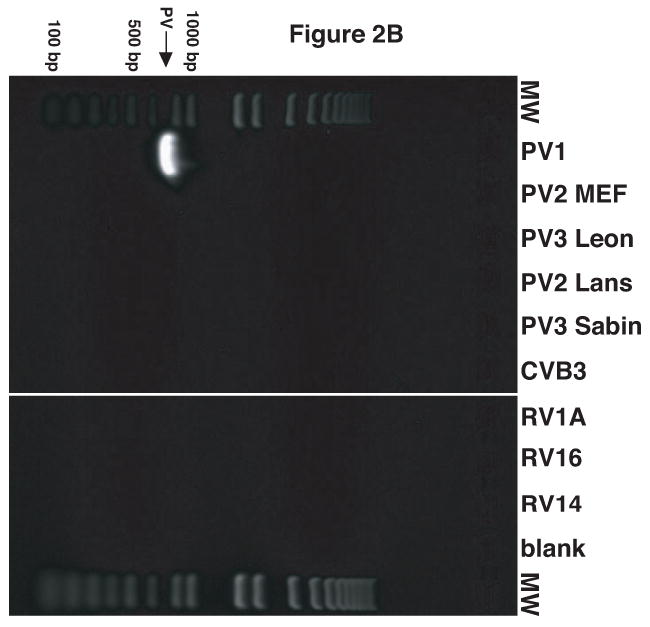
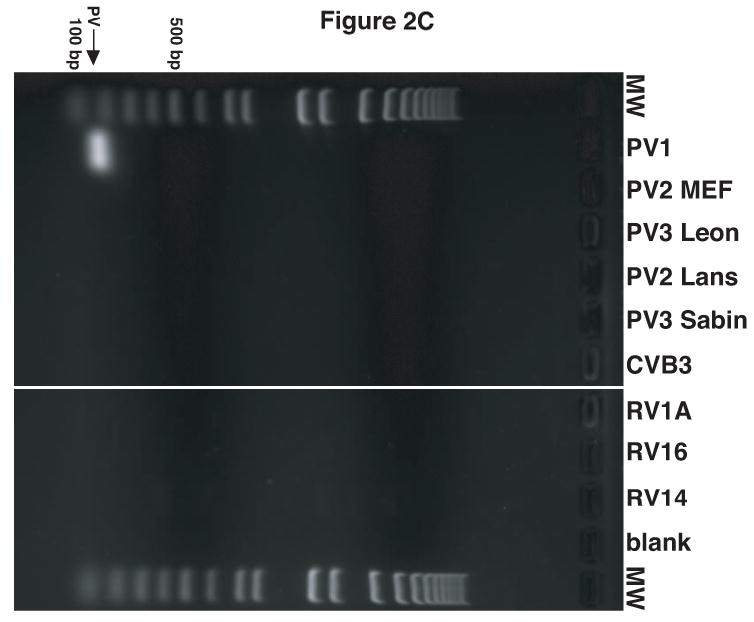
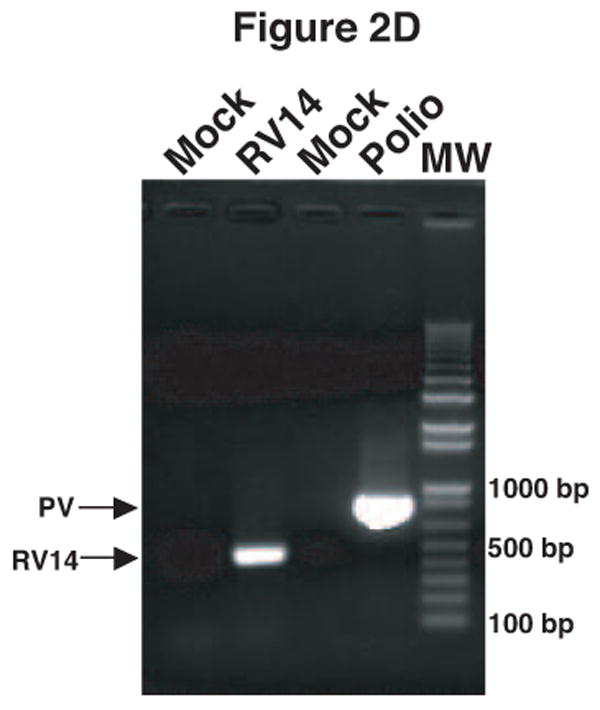
Validation of RV14 and PV1 primers. Conventional PCR was conducted using RV14 primers (A), PV1 primers (B) and PV1 nested PCR primers (C) and DNA templates harboring the sequences from the indicated viruses; Poliovirus type 1 (PV1), Poliovirus type 2 MEF-1 strain (PV2 MEF), Poliovirus type 3 Leon strain (PV3 Leon), Poliovirus type 2 Lansing strain (PV2 Lans), Poliovirus type 3 Sabin strain (PV3 Sabin), Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3) and human rhinovirus types 1A, 16 and 14 (HRV1A, HRV16 and HRV14. Ethidium bromide stained agarose gels show the location of the 465 bp rhinovirus (RV14) (A) and 798 and 171 bp poliovirus (PV1) (B and C, respectively) specific amplicons. Blank indicates no template was added to the PCR reaction. MW; molecular weight markers. D. Identification of RV14 and PV1 from infected cells. Total RNAs extracted from uninfected, RV14 or PV-infected cells were reverse transcribed into cDNA and analyzed by PCR with primers for both RV14 and PV1. Labeling and analysis is as described above.
