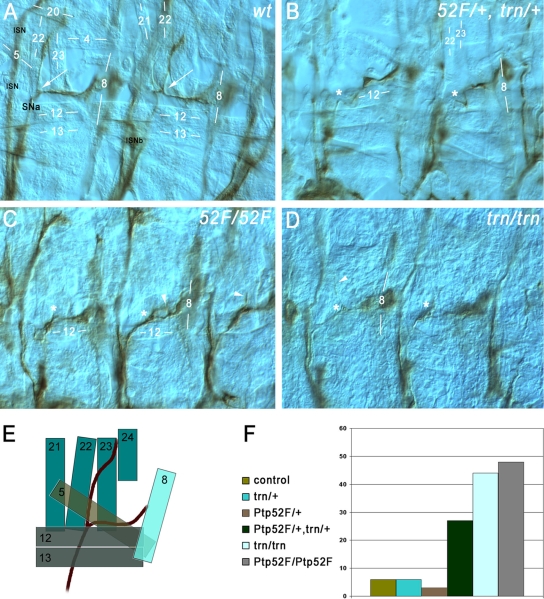
FIG. 5.
Ptp52F and tartan mutants have the same motor axon guidance phenotypes, and the genes display a dosage-dependent interaction. Motor axons (brown) in late-stage 16/early-stage 17 embryo “fillets” were stained with MAb 1D4, using HRP immunohistochemistry for visualization, and photographed using differential interference contrast optics. (A) Two hemisegments in a wild-type (wt) control embryo. SNa, the branch that exhibits phenotypes in both of these mutants, is labeled. Its bifurcation point is indicated by white arrows in both segments. The ISN and ISNb (out of focus) are also labeled. Muscle fibers are labeled by number (compare to diagram of panel E). The anterior SNa branch normally extends dorsally along muscle 22 and then across muscle 23 to reach muscle 24, and the posterior branch extends across muscle 5 to reach muscle 8. (B) Two hemisegments in a Ptp52F/+, trn/+ embryo (lacking one wild-type copy of each gene). The anterior branch of the SNa is missing in both segments. The approximate points at which bifurcation would have occurred if the anterior branches were present are indicated by asterisks. (C) Three hemisegments in a Ptp52F/Ptp52F embryo. The anterior branch of the SNa is missing, truncated, or misguided in all three. In the left-hand hemisegment the branch is missing, while in the middle hemisegment axons branch off near the normal bifurcation point (asterisks) but then grow posteriorly and rejoin the posterior SNa branch, forming a loop (arrowhead). In the right-hand hemisegment a thin and truncated anterior branch is observed (arrowhead). (D) Two hemisegments in a trn/trn embryo. In the right-hand segment, the anterior branch is missing, while in the left-hand hemisegment a single axon appears to have extended partway along the normal anterior branch pathway (arrowhead), leaving the SNa near the normal bifurcation point (asterisks). (E) Diagram of the SNa and adjacent muscle fibers in wild-type. The muscles are indicated as semitransparent to show their layering. The deepest (most external) muscles are 21 to 24, and they are overlaid by muscles 5, 12, 13, and 8. SNa extends underneath (external to) 12 and 13. (F) Bar graph of phenotypic penetrance for SNa guidance errors, in control (balancer/+); trn/+; Ptp52F/+; Ptp52F/+, trn/+; trn/trn; and Ptp52F/Ptp52F cells. The numbers of hemisegments examined and the distribution among phenotypic classes are shown in Table 2.