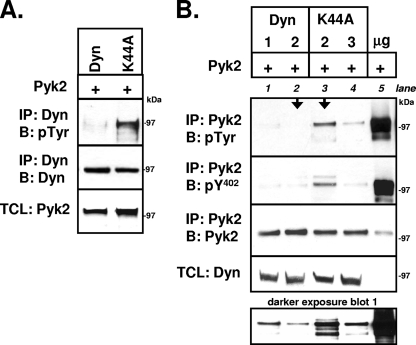
FIG. 2.
Dynamin reduces phosphorylation of Pyk2-Y402. (A) 293VnR cells were transiently cotransfected with Pyk2 and either dyn-GFP or dynK44A-GFP. Dynamin and dynK44A were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP and resolved by SDS-PAGE, and Western blot analysis was performed with an antiphosphotyrosine (anti-pTyr) antibody. Immunoprecipitates were reblotted for dyn-GFP with anti-GFP, while TCLs were blotted for Pyk2. Representative blots of 10 independent experiments are shown. (B) Increasing amounts of dyn-GFP (1 and 2 μg) or dynK44A-GFP cDNA (2 and 3 μg) were transiently cotransfected with constant amounts of Pyk2 cDNA (3 μg) into 293VnR cells. Empty vector was used to keep total transfected cDNA constant. Immunoprecipitation of Pyk2 was performed, followed by SDS-PAGE. Western blot analyses of immunoprecipitates, followed by stripping and reblotting was performed consecutively with an anti-pTyr), an anti-Pyk2-phospho-Y402 (pY402), and an anti-Pyk2 antibody. Transiently expressed Pyk2 undergoes robust phosphorylation in the absence of dynamin proteins (lane 5) (30% of the immunoprecipitate was loaded). However, coexpression of wild-type dynamin (lanes 1 and 2) or mutant dynamin (lanes 3 and 4) caused a dose-dependent decrease in total phosphorylated Pyk2 (blot 1, top) and phosphorylated Pyk2-Y402 (blot 2, bottom). Dynamin reduced Pyk2 phosphorylation to a greater degree than dynK44A when similar amounts of cDNA were transfected (arrows). Representative blots from five independent experiments are shown. Molecular mass markers are indicated. Labels: IP, immunoprecipitation; B, Western blot; Dyn, dynamin.