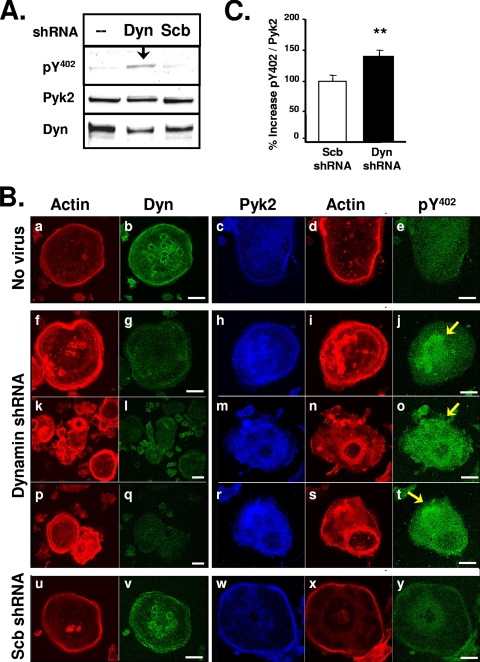
FIG. 3.
Dyn-shRNA increases Pyk2 Y402 phosphorylation in OCLs. (A) OCLs were prepared as described in Materials and Methods and were left uninfected or were infected with dyn-shRNA or scrambled (scb)-shRNA adenoviruses. Cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and blotted with antibodies to phospho-Pyk2-Y402, Pyk2 or dynamin. (B) OCLs were uninfected (a to e) or infected with adenoviruses expressing shRNA to dynamin-2 (dyn-shRNA) (f to t) or a scrambled sequence (scb-shRNA) (u to y) for 3 days. Infected cells were replated on glass coverslips for 24 h, fixed, and immunolabeled for dynamin, Pyk2, phosphorylated Pyk2-Y402, or actin (rhodamine phalloidin, red) as indicated. Cells were visualized by scanning confocal immunofluorescence microscopy. Scale bars, 20 μm. Experiments were repeated at least three times and representative cell images are shown. The cells shown in panels f to j, k to o, and p to t are separate representative images of dyn-shRNA-infected cells. Arrows indicate increased levels of phospho-Y402 in dyn-shRNA-infected cells. (C) The change in the phosphorylation of Pyk2 Y402 in dyn-shRNA-infected OCLs was determined by normalizing the fluorescence intensity of anti-phospho-Y402 staining to the fluorescence intensity of anti-Pyk2 staining in double-labeled dyn-shRNA-infected OCLs. The fluorescence intensity of a minimum of seven cells from three different experiments was measured (error bars represent the standard error of the mean [SEM]; *, P < 0.05 [Student t test]). The specificity of the phospho-Y402 antibody for Pyk2 that was used for labeling the OCLs was confirmed by Western blot analysis of Pyk2 and Pyk2-Y402F expressed in 293VnR cells (see Fig. S1 in the supplemental material). Dyn, dynamin.