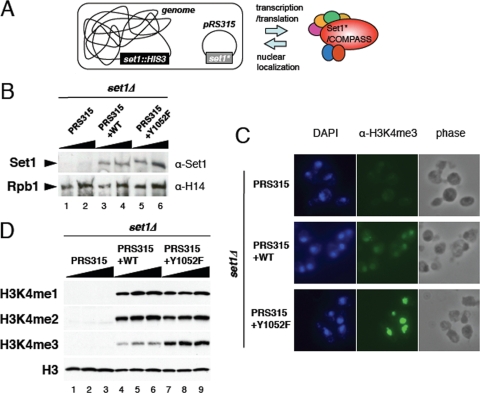
FIG. 2.
H3K4 methyltransferase activity of the Set1 Y1052F mutant in vivo. (A) Schematic representation of the yeast construct used for the mutational analyses of the SET domain of Set1. Yeast cells with the genomic SET1 gene replaced with the HIS3 marker are transformed with low-copy-number plasmid pRS315 harboring the SET1 coding sequence together with its own preceding promoter region, enabling an expression level equivalent to that of exogenous Set1. Point mutations were introduced into the SET1 gene carried on plasmid pRS315 (Set1*). (B) Wild-type (WT) and mutant Set1 levels in the different strains. Cell extracts prepared from logarithmically growing cells harboring SET1 plasmids were analyzed by Western blotting using polyclonal antibodies specific to Set1. H14 Western blotting detecting the large subunit of RNA Polymerase II (Rpb1) levels was used as a loading control. (C) Immunofluorescence analyses of H3K4 trimethylation by COMPASS containing wild-type or single point mutant Set1 proteins. Paraformaldehyde-fixed yeast cells were stained with DAPI and primary mouse antibodies toward trimethylated H3K4 and fluorescein-conjugated secondary antibodies. Phase-contrast images are shown in the right-hand panels. (D) Analyses of H3K4 methylation on bulk histones from cell extracts using anti-H3K4me1, anti-H3K4me2, and anti-H3K4me3-specific antibodies. Equal quantities of cell extracts from cells expressing both wild-type and mutant Set1 were subjected to SDS-PAGE, followed by Western blotting. α, anti; WT, wild-type Set1. Triangles represent increasing sample loads.