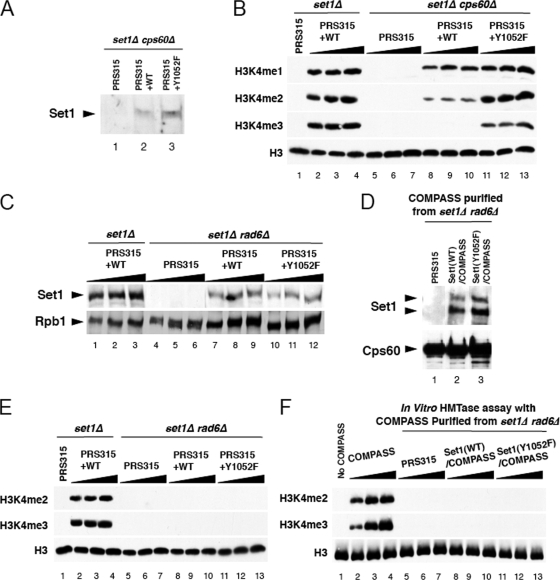
FIG. 5.
Y1052F Set1 suppresses H3K4 di- and trimethylation defects in a cps60 (bre2) null strain, while H3K4 methylation loss caused by the loss of Rad6 is refractory to this mutation. (A) Wild-type and Y1052F mutant Set1 protein expression in a cps60 (bre2) null strain was confirmed by Western blotting with anti-Set1 antibody. (B) In vivo H3K4 methylation status in the cps60 deletion background. Assays were performed as described for Fig. 2D, except with set1 and cps60 double null cells as the genetic background. (C to F) Y1052-mediated H3K4 trimethylation regulation is independent of H2B K123 monoubiquitination via the Rad6/Bre1 pathway. (C) Equal expression of wild-type and Y1052F mutant Set1 introduced in a rad6 set1 double knockout strain as determined by Western analysis. Antibody H14, detecting Rbp1, was used as a loading control. (D) The levels of Set1 within COMPASS purified from either the wild type or rad6Δ strain carrying the vector containing either wild-type Set1 or Y1052F mutated Set1 or the vector only were examined by Western blotting using polyclonal antibodies specific to Set1. (E) Bulk H3K4 methylation levels were determined in a set1Δ strain expressing wild-type Set1 from a plasmid or a set1Δ rad6Δ strain expressing wild-type or Y1052F mutant Set1 from this vector or the vector only. (F) Wild-type or Y1052F Set1-containing COMPASS, purified from Cps60-TAP strains with RAD6 deleted, was tested for histone methyltransferase (HMTase) activity in vitro. Similar to the results of the in vivo studies described for panel E, Set1(Y1052F) cannot compensate for the loss of Rad6 in vitro. Triangles represent increasing loads of extracts. PRS315, plasmid pRS315; WT, wild-type Set1.