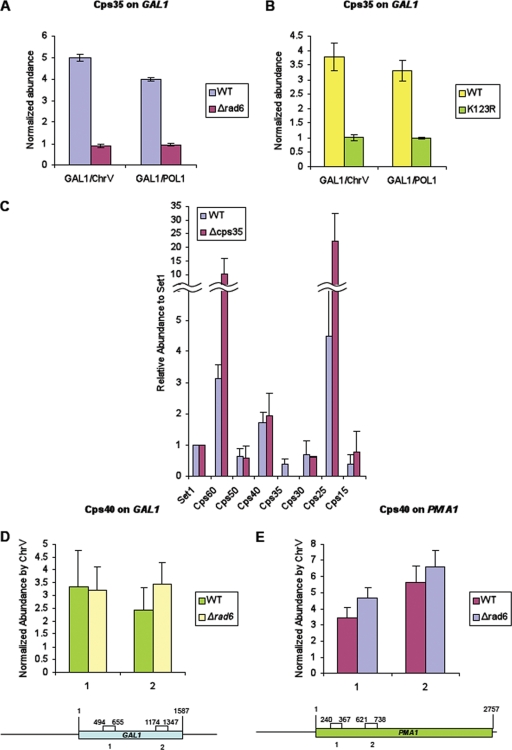
FIG. 6.
Cps40 (Spp1) can interact with COMPASS independently of monoubiquitinated histone H2B and Cps35 (Swd2). (A and B) ChIP of the GAL1 gene through myc-tagged Cps35 in the presence and absence of ubiquitinated H2B. Myc-Cps35 ChIP from wild-type (WT) and rad6Δ (A) and H2B(K123R) (B) strains. ChIP enrichments were normalized to the level in a ChrV nontranscribed intergenic region or the POL1 open reading frame. (C) Purification of Cps60-TAP tagged COMPASS from the wild-type (WT) and a Cps35 null strain (19). All COMPASS components except Cps35 can be detected in COMPASS purified from the cps35 null strain, indicating that Cps40 (Spp1) does not interact with COMPASS in a Cps35 (Swd2)-dependent manner. Using spectral counts, the composition of COMPASS purified from Cps35 null strain was determined (14). This histogram shows the abundances of COMPASS components purified from a cps35 null strain relative to those from the wild-type strain relative to the level of Set1. (D and E) ChIP of GAL1 (D) and PMA1 (E) genes for Cps40 in the presence and absence of monoubiquitinated H2B. Cell extracts were prepared from strains expressing nine-Myc-tagged Cps40 in the presence (wild type; WT) and absence of Rad6. (D) ChIP assay for Cps40 on the GAL1 gene was performed similarly to the ChIP assay described for Cps35 of the GAL1 gene whose results are shown in panels A and B. (E) ChIP of Cps40 on the PMA1 gene. Cells were grown in a dextrose-containing medium to an OD600 of 1.0, followed by formaldehyde-based in vivo cross-linking. Immunoprecipitations and qPCR were performed as described for panels A and B. ChIP enrichments were normalized to the levels in a ChrV nontranscribed intergenic region. Error bars show standard deviations.