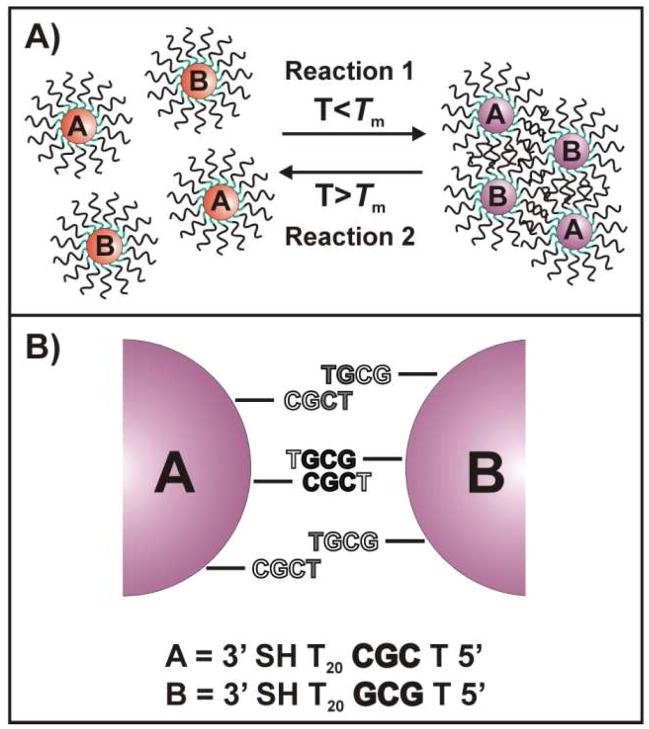
Scheme 1.
A) General scheme for the hybridization and melting of particles which are functionalized with complementary oligonucleotide sequences termed A and B. B) General scheme (in a ‘two-particle’ model) showing the potential interactions (normal and “slipping”) accessible for DNA-AuNPs functionalized with TCGC– (particle A) and TGCG– (particle B). The interactions possible for oligonucleotides on the particle surface depend on their ability to engage in hybridization with complementary strands on an adjacent particle and are impacted by the radius of curvature of the particles. Black lettering indicates bases involved in normal Watson-Crick interactions, gray lettering indicates bases involved in non-Watson-Crick “slipping” interactions, and white lettering indicates bases that are not involved in hybridization.