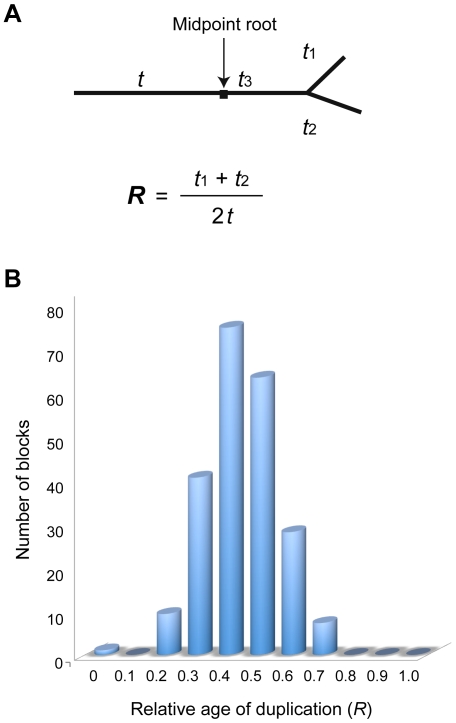
Figure 3. Estimation of duplication dates using P. blakesleeanus as an outgroup.
(A) An unrooted tree diagram for the duplicated gene pairs in R. oryzae and their homologous gene in P. blakesleeanus. Midpoint rooting is used to calculate of the relative age of each duplication (R) in relation to the root. The branch lengths as substitutions per site for the unrooted tree topology were calculated using the WAG evolutionary model [49] employing a maximum likelihood-based package, PhyML [50]. The distance between two duplicated genes in R. oryzae is t 1+t 2, and the distances between the duplicates and their orthologous gene in P. blaskesleeanus are t+t 3+t 1 and t+t 3+t 2, respectively. (B) The distribution of the relative duplication time for each duplicated region in comparison to the root (R). R is normalized within each duplicated region by averaging the divergences of all the duplicated gene pairs within the region. If the divergence time between R. oryzae and P. blakesleeanus is defined as t using midpoint rooting, approximately 78% of all these regions were estimated to be duplicated within one standard deviation (0.115) of the mean (0.386t).