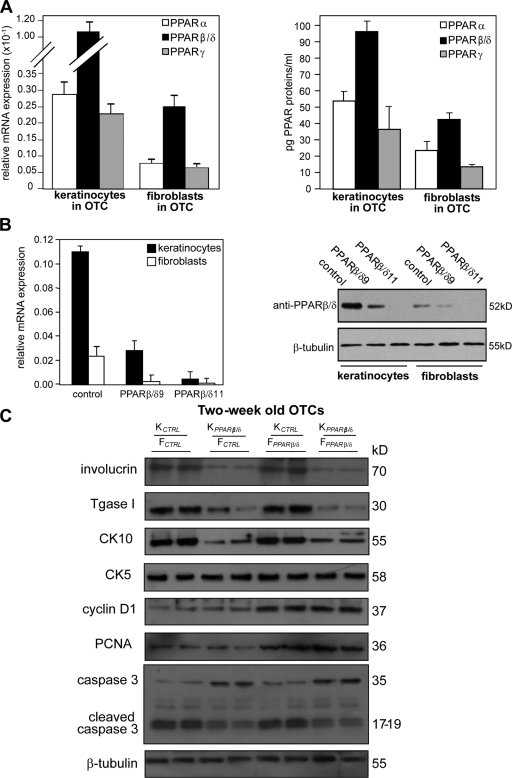
Figure 1.
PPARβ/δ-deficient fibroblasts increase epidermal proliferation. (A) Expression profile of PPARs in OTC keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Total RNA and protein were extracted from keratinocytes and fibroblasts in OTC. Expression levels of PPAR mRNA (left) and protein (right) were monitored by qPCR and PPAR transcription factor assay kit, respectively. PPARβ/δ mRNA was normalized with control ribosomal protein P0 mRNA. (B) Human keratinocytes or fibroblasts were transduced with a lentiviral vector harboring a control or two different PPARβ/δ (PPARβ/δ9 and PPARβ/δ11) siRNAs. (C) Immunoblot analysis of epidermis from 2-wk-old OTCs constructed using KCTRL or KPPARβ/δ and FCTRL or FPPARβ/δ. Involucrin and transglutaminase I (Tgase I) are terminal differentiation markers, and keratin 10 (CK10) is an early differentiation marker. Keratin 5 (CK5) identifies the basal keratinocytes. Cell proliferation was measured using PCNA and cyclin D1. Apoptosis was detected using caspase 3. β-Tubulin showed equal loading and transfer. Representative immunoblots of epidermis from two OTCs are shown. Data are mean ± SD, n = 3.