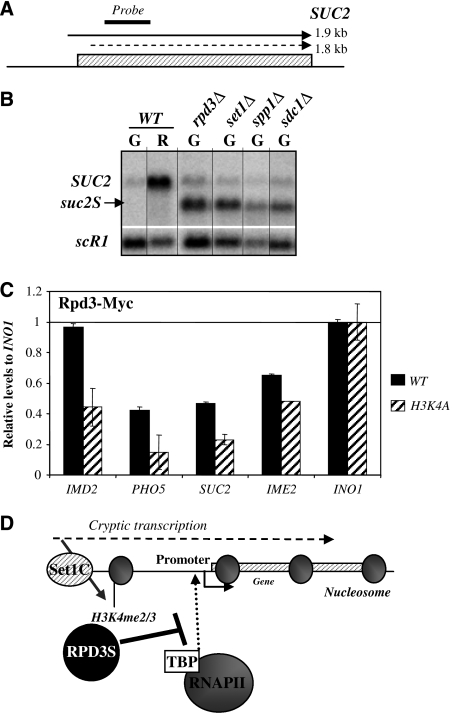
Figure 7.
H3K4me2/3 recruit Rpd3 to control SUC2 promoter fidelity. (A) Schematic view of the SUC2 transcripts with positions of the probes for northern blot and qPCR. (B) Set1-dependent H3K4me2/3 repress a SUC2 spurious transcript (suc2S). Northern blot with total RNAs extracted from WT (YAM1 and 92), rpd3Δ (YAM4), set1Δ (YAM249) spp1Δ (YAM804) and sdc1Δ (YAM800) strains. WT cells were grown in glucose (G) and transferred in raffinose (R) containing media. Mutants were grown in glucose containing media (G) only. scR1 is a loading control and SUC2 has been probed according to Figure 7A. (C) Rpd3-Myc is targeted to SUC2, IMD2 and PHO5 promoters and is dependent on H3K4me. Chromatin immunoprecipitant (ChIP) experiments were performed with an anti-Myc antibody in WT (YAM1477) and H3K4A (YAM1481) strains in glucose. Amplicons correspond to SUC2, PHO5, IMD2, IME2 and INO1 promoters. Results are presented as percentage of input normalized with the promoter of INO1. (D) Model of promoter attenuation by H3K4me2/3. Cryptic transcription activates the deposition of H3K4me2/3 on promoter proximal regions and triggers the recruitment of the RPD3S complex inhibiting the pre-initiation complex (PIC) formation and promoter activity.