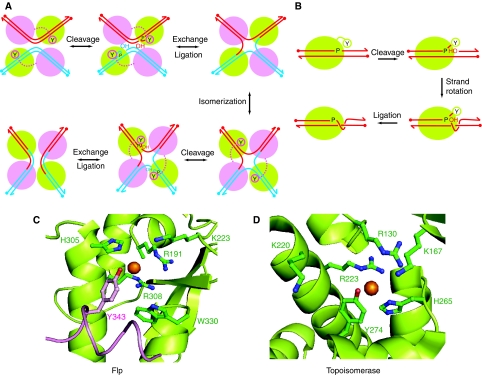
Figure 1.
Reaction pathways and active site configurations for tyrosine site-specific recombinase and type IB topoisomerase reactions. (A) Recombination by Flp site-specific recombinase proceeds through the following steps: (a) single strand cleavages; (b) strand exchange and formation of a Holliday junction intermediate; (c) isomerization of the Holliday junction; (d, e) resolution of the junction into recombinant products. Two Flp monomers (green) activate the scissile phosphodiester bonds in cis, and the other two (magenta) donate the tyrosine nucleophile in trans. (B) A round of DNA relaxation by vaccinia topoisomerase I proceeds through (a) single strand cleavage, (b) strand rotation and (c) strand religation. Activation of the scissile phosphodiester and strand cleavage is mediated in cis by a single topoisomerase monomer. (C) In the Flp active site (Chen et al, 2000), the catalytic pentad of Arg-191, Lys-223, His-305, Arg-308 and Trp-330 are derived from one Flp monomer (green), and Tyr-343 poised to attack the scissile phosphate (gold sphere) is supplied by the neighbouring Flp monomer (magenta). (D) The active site of the small pox virus topoisomerase enzyme shown here (Perry et al, 2006) is functionally related to that of vaccinia topoisomerase (Cheng et al, 1998). It is characterized by a catalytic pentad of Arg-130, Lys-167, Lys-220, Arg-223 and His-265 plus Tyr-274, all derived from a single topoisomerase monomer.