Figure 3.
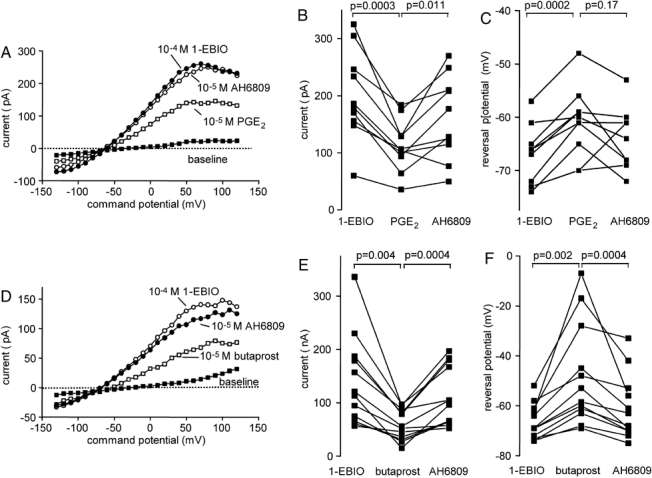
The effect of the EP1/2 receptor antagonist AH6809 on PGE2- and butaprost -dependent closure of KCa3.1. (A) Current–voltage curve demonstrating reversibility of KCa3.1 suppression by PGE2 following administration of the EP1/2 receptor antagonist AH6809. (B) KCa3.1 current measured at +40 mV after addition of 1-EBIO, suppression by 10−5 M PGE2 and then reversibility of suppression following addition of AH6809 (n=10 cells). (C) Whole-cell current reversal potential (Vm) after the addition of 1-EBIO, a depolarising positive shift in response to 10−5 M PGE2, and then following addition AH6809 (n=10 cells). (D) Current–voltage curve demonstrating reversibility of KCa3.1 suppression by butaprost following administration of AH6809. (E) KCa3.1 current measured at +40 mV after addition of 1-EBIO, suppression by 10−5 M butaprost and then reversibility of suppression following addition of AH6809 (n=12 cells). (F) Whole-cell current reversal potential (Vm) after the addition of 1-EBIO, a depolarising positive shift in response to 10−5 M PGE2, and then reversibility following addition AH6809 (n=12 cells).
