Figure 1. EBF expression restores B-cell development from Ikzf1-/-hematopoietic progenitors.
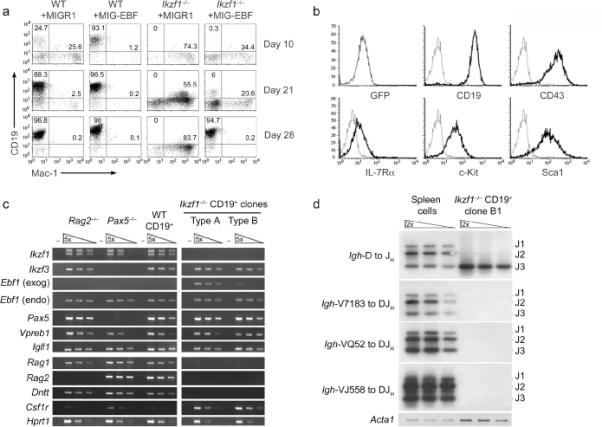
(a) Kinetic analysis of B cell development induced by the expression of EBF in Ikzf1-/- LSK progenitors. Wild-type or Ikzf1-/- LSK progenitors were transduced with MIGR1 or MIG-EBF viruses and cultured on OP9 stromal cells under B lymphoid conditions. Cultures were harvested at day 10, 21 and 28 and analyzed for generation of B lymphoid (CD19+) or myeloid (Mac-1+) precursors. (b) Flow cytometry of an Ikzf1-/- CD19+ clonal cell line rescued with EBF. (c) Gene expression analysis of Ikzf1-/- CD19+ clones. Type A clones express both exogenous (exog) and endogenous (endo) Ebf1 genes whereas type B clones only express the latter. Serial dilutions of cDNA were analyzed by RT-PCR after normalization to Hprt1. cDNAs from wild-type CD19+ cells generated in vitro (denoted WT CD19+) as well as Rag2-/- and Pax5-/- pro-B cell lines were used as controls. (d) PCR analysis of Igh rearrangements. Genomic DNA from Ikzf1-/- CD19+ clone B1 was analyzed using primers that detect DH to JH or VH7183-, VHQ52- and VHJ558-to-DJH rearrangements. PCR products were detected by Southern blotting. Genomic DNA from spleen cells was used as a control. DNA samples were normalized with Acta1 (encoding α-actin). All data are representative of at least two independent experiments.
