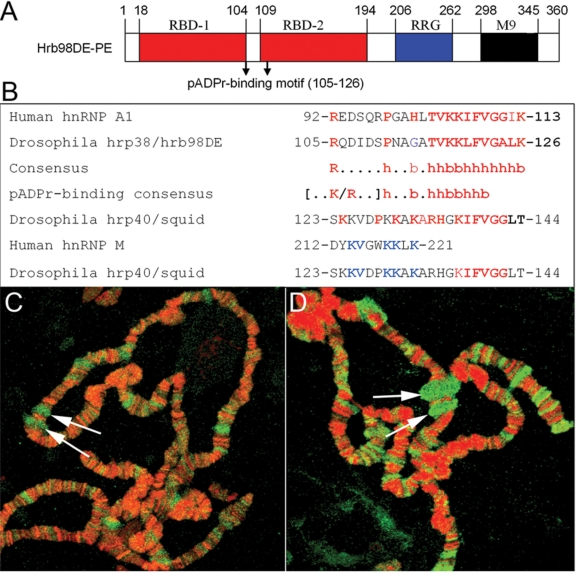
Figure 1.
The pADPr-binding motif in Drosophila Hrp38 and Squid protein. (A) Conserved functional domains of Drosophila hrp38 protein. RBD: RNA-binding domains. RGG: glycine-rich domain. M9: nuclear shuttling signal domain. (B) Alignment of putative pADPr-binding sequences of human and Drosophila hnRNPs with the consensus of pADPr-binding motif. The conserved residues in the pADPr-binding motif among human hnRNP A1, hrp38 and Squid are marked in red; among human hnRNP M and Drosophila Squid, they are marked in blue (b: basic, h: hydrophobic amino acid). (C) The accumulation of pADPr in the puffs. Drosophila polytene chromosomes of the wild-type line (y,w) were immunostained with the anti-pADPr antibody (10H). pADPr: green; DNA: red. (D) The localization of Squid in the puffs. Drosophila polytene chromosomes of the wild-type line (y,w) were immunostained with the anti-Squid antibody. Squid: green; DNA: red. Arrows in (C) and (D) indicate the E74 and E75 puffs.