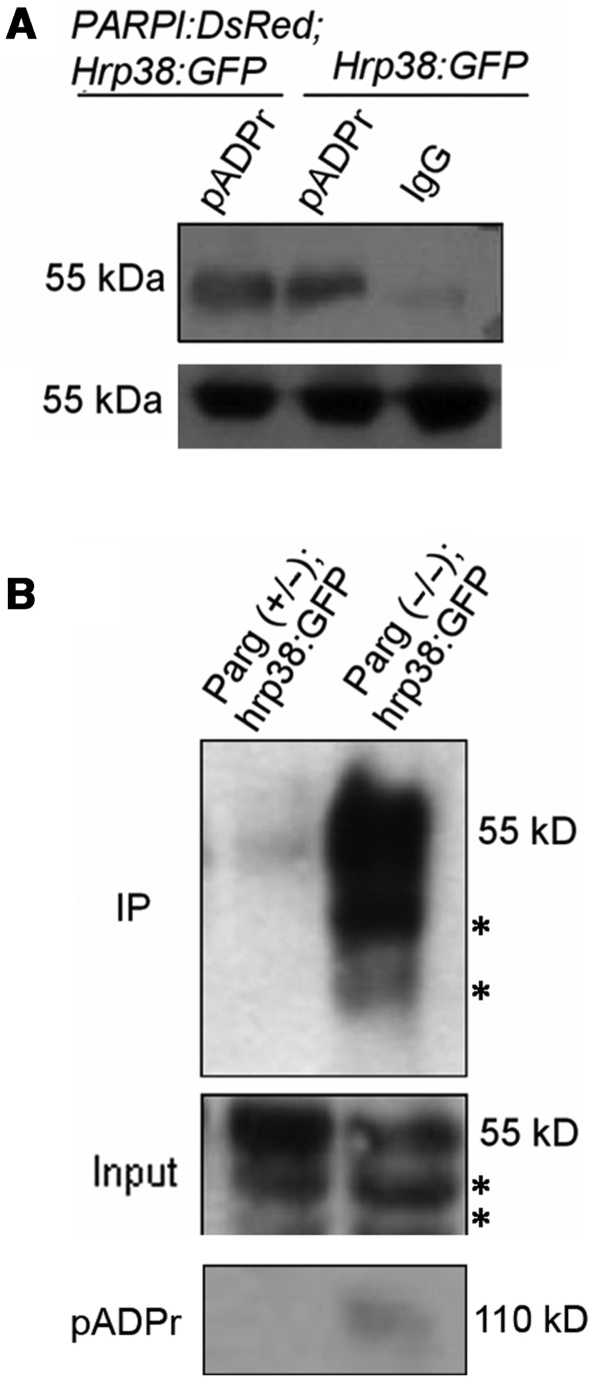
Figure 3.
Increased amounts of hrp38 bound to pADPr in vivo by PARP overexpression and Parg mutation. (A) Equal lysates of hrp38:GFP and PARP1-DsRed; hrp38:GFP transgenic lines were immunoprecipitated using rabbit anti-pADPr antibody or the preimmune IgG crosslinked to protein A agarose beads. The immunoprecipitates and 5% input for immunoprecipitation were subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-GFP antibody. (B) Equal amounts of the lysates from Parg+/− heterozygote and Parg−/− homozygotes were immunoprecipitated using rabbit anti-pADPr antibody crosslinked to protein A agarose beads. The immunoprecipitates (upper panel) and 5% input for immunoprecipitation (middle panel) were subjected to immunoblot analysis using anti-GFP antibody. The same blot in the upper panel was stripped and probed with anti-pADPr monoclonal antibody (bottom panel). Asterisk in upper and middle panel indicates the degraded products from hrp38:GFP.