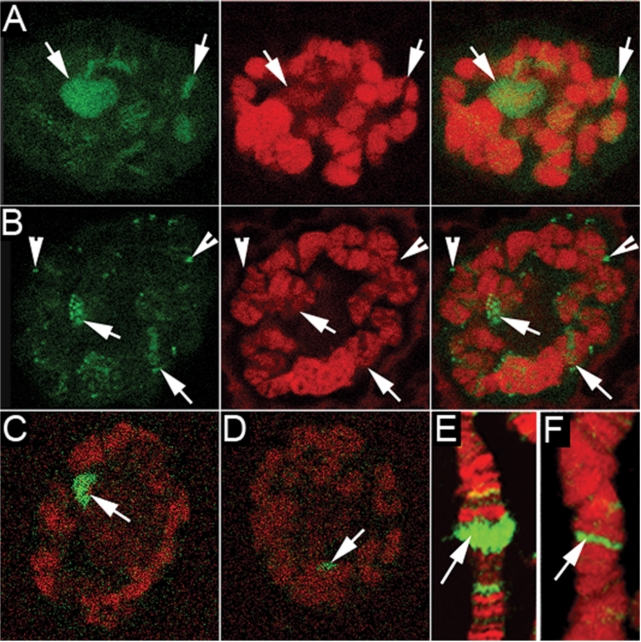
Figure 6.
The dissociation of hrp38 and Squid from the puffs in polytene chromosomes caused by heat shock and Parg null mutation: hrp38:GFP from the intact nuclei is shown as green in (A) through (D). Squid from the squashed nuclei is shown as green in (E) and (F). DNA is shown as red in (A) through (F). All images are from a single confocal section. (A) The localization of hrp38:GFP in the salivary glands polytene chromosomes of the hrp38:GFP transgenic line (ZCL588). Arrows indicate the major puffs. (B) The dissociation of hrp38:GFP from the puffs in polytene chromosomes of Parg27.1; hrp38:GFP transgenic lines. Arrowheads indicate extrachromosomal particles accumulating HRP proteins. (C) hrp38:GFP binding to the 93D puff in polytene chromosomes of the hrp38:GFP line after heat-shock treatment. Arrow indicates the 93D puff in (C) through (F). (D) Reduced amounts of hrp38:GFP binding to the 93D puff in the Parg27.1; hrp38:GFP line after heat-shock treatment. (E) Squid binding to the 93D puff in polytene chromosomes of the wild-type line (yw) after heat-shock treatment: Squid, green; DNA, red. (F) Reduced amounts of Squid binding to the 93D puff in the Parg27.1 line after heat-shock treatment: Squid, green; DNA, red.