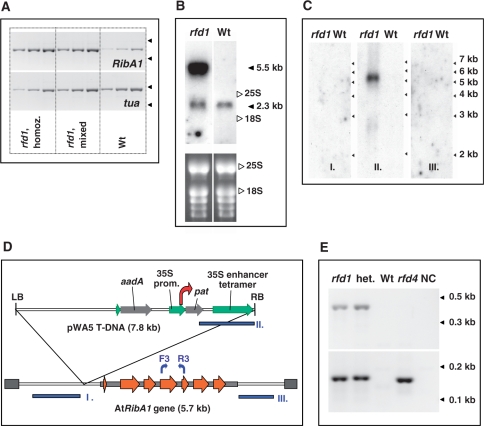
Figure 2.
(A) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of etiolated seedlings. Homozygous (rfd1, homoz.) as well as nonfluorescent (rfd1, mixed) rfd1 seedlings were collected and compared to A. thaliana wild-type seedlings (Wt). Accumulation of AtRibA1 (RibA1, upper panel) and alpha-tubulin (tua, lower panel) transcripts was investigated using primer pairs F3/R3 (see Figure 2D) and tuaF/tuaR, respectively. Reverse-transcribed total RNA measuring 2 ng, 6 ng and 18 ng (from left to right) were used as template. Arrowheads on the right side of each panel indicate the migration of 0.4-kb and 0.3-kb marker fragments. Note that, due to segregation, the nonfluorescent sample (rfd1, mixed) contained heterozygous rfd1 as well as wild-type seedlings. (B) Northern blot of RNA isolated from heterozygous rfd1 mutants (rfd1) and A. thaliana wild type (Wt) was hybridized to AtRibA1 cDNA. 25S rRNA (3.3 kb) and 18S rRNA (1.7 kb) positions as well as the estimated sizes of specific bands are indicated. The lower panel depicts an ethidium bromide stain of RNA before blotting. (C) Hybridization of RNA blots of heterozygous rfd1 mutants and A. thaliana wild type (Wt) with probes I, II and III, respectively. (D) Localization of DNA fragments I, II and III (blue boxes) used as probes in (C); positions of primers for sq RT-PCR of AtRibA1 (F3, R3) are indicated by blue arrows. The transcription start site of the 5.5-kb T-DNA:AtRibA1 fusion transcript identified in line rfd1 is indicated by a red arrow. (E) 5′ RACE of the pat gene in homozygous (rfd1) or heterozygous (het.) rfd1 mutant plants, compared to A. thaliana wild type (Wt) and an alternative T-DNA insertion line carrying the pWA5 plasmid (rfd4). Primary RACE PCR (upper panel) was performed with 35 cycles using primers Ad1 and pat_RACE351. The secondary, nested amplification used Ad2 and pat_RACE113 and 25 additional cycles (lower panel). A non-template control is shown in lane NC. Fragment lengths are indicated by arrowheads at the right margin.