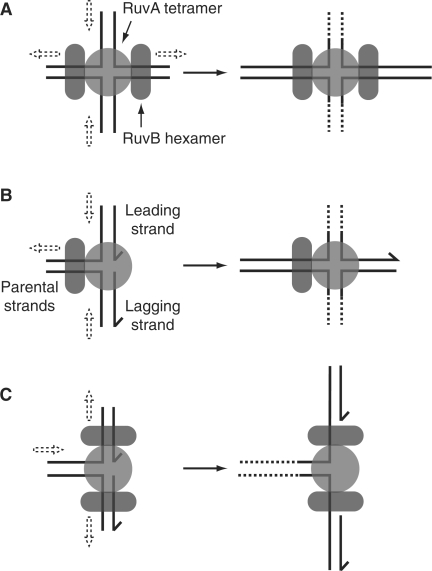
Figure 4.
Action of RuvAB on Holliday junctions and forks. (A) Action of RuvAB on Holliday junction structures. Translocation of the two RuvB hexamers along opposing duplex arms results in movement of duplexes as indicated by dashed arrows. Strand separation results from spooling of the DNA strands across the ‘acidic pins’ found on the surface of the RuvA tetramer (176). (B) Catalysis of fork regression by RuvAB would necessitate loading of a single RuvB hexamer onto the parental duplex. (C) Binding of two RuvB hexamers onto opposing duplex arms of a fork would result in unwinding of the junction in the direction opposite to that required for regression.