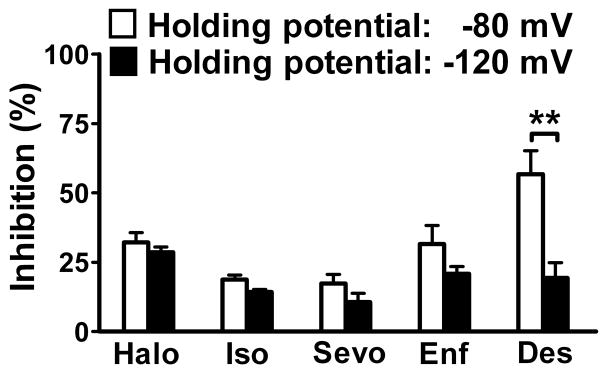
Fig. 2.
Voltage-dependent inhibition of Nav1.4 by inhaled anesthetics. Equipotent concentrations (~1 MAC) of inhaled anesthetics differentially inhibited INa from a holding potential of −80 mV (open bars) or −120 mV (filled bars). The measured concentrations of halothane (Halo), isoflurane (Iso), sevoflurane (Sevo), enflurane (Enf), and desflurane (Des) were 0.42±0.05 mM (1.2 MAC), 0.46±0.03 mM (1.3 MAC), 0.44± 0.03 mM (1.0 MAC), 0.82±0.04 mM (1.1 MAC), and 0.83±0.03 mM (1.0 MAC), respectively, from a holding potential of −80 mV; and were 0.38±0.05 mM (1.1 MAC), 0.41±0.04 mM (1.1 MAC), 0.45±0.05 mM (1.0 MAC), 0.80±0.05 mM (1.1 MAC), and 0.83±0.04 mM (1.0 MAC), respectively, from a holding potential of −120 mV. Data are expressed as mean±SEM (n=4–12). ** P < 0.01 by unpaired t-test.