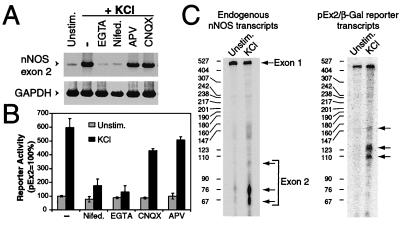
Figure 3.
nNOS mRNA is regulated by Ca2+ influx through L-type VSCCs. (A) Blocking Ca2+ influx inhibits nNOS exon 2 mRNA expression. RT-PCR analysis of nNOS exon 2 mRNA after membrane depolarization was carried out in the presence or absence of EGTA (2 mM), nifedipine (100 μM), 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV; 25 μM), or 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX; 25 μM). GAPDH was used as a control for RNA input and reverse transcription efficiency. PCR products were visualized by PhosphorImager analysis. This experiment was replicated two times with similar results. (B) Preventing Ca2+ influx blocks nNOS exon 2 reporter activity. Cortical neurons were transfected with the nNOS exon 2 β-gal reporter construct (pEx2). Before membrane depolarization, cells were left untreated (−) or treated with same drugs as in A. Each value is the average of three to five independent determinations, and the error bars indicate the SEM. (C) Mapping of transcription initiation sites. Cortical neurons were either transfected with the pEx2 construct or left untreated. Two days later the cells were treated with 50 mM KCl (6 h) or were unstimulated, and total RNA was isolated. S1 nuclease-protection assays were performed with probes selective for nNOS exon 2 and pEx2-β-Gal. Transcription start sites are indicated by arrows. The sizes (bp) of the RNA ladder are indicated by the numbers in the left margin. This experiment was replicated three times with similar results.