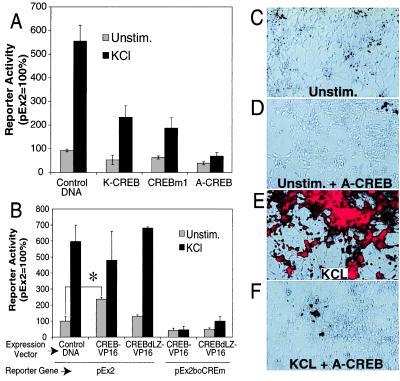
Figure 5.
A CREB family member mediates nNOS transcription after membrane depolarization. (A) Overexpression of dominant-negative K-CREB, CREBm1, or A-CREB inhibits promoter activation. K-CREB, CREBm1, or A-CREB expression and control vectors were cotransfected with pEx2 into cultured cortical neurons. Two days after transfection, cells were left unstimulated or stimulated with 50 mM KCl for 12 h. Cell extracts were then assayed for β-gal and luciferase activities. Each value is the average of at least three to five independent determinations, and the error bars indicate the SEM. (B) A constitutively active CREB triggers Ca2+-independent promoter activation. Cultured cortical neurons were transfected with the indicated constructs, and β-gal and luciferase activities were assayed. CREB-VP16 contains full-length CREB and the transcriptional activation domain of VP16, a potent herpes virus transcriptional activator. CREBdLZ-VP16 is similar to CREB-VP16 except that the DNA-binding domain and dimerization domain of CREB are deleted. Each value is the average of at least three to five independent determinations, and the error bars indicate the SEM. ∗, P ≤ 0.002. (C–F) Dominant-negative A-CREB attenuates KCl-induced expression of the endogenous nNOS. Cultured cortical neurons were coinfected with AdVgRXR and AdEGI-control or AdEGI-A-CREB viruses and treated with muristerone to induce transgene expression. Twenty-four hours later cortical neurons were left unstimulated or were stimulated with 50 mM KCl. nNOS expression was monitored by immunofluorescence with merged Hoffman modulation/immunofluorescence photomicrographs. Unstimulated neurons infected with control viruses (AdVgRXR and AdEGI-control) show a modest amount of nNOS immunostaining in the absence of stimulation (C), but in response to membrane depolarization show striking nNOS immunoreactivity (D). In contrast, neurons infected with viruses containing A-CREB and VgRXR show minimal nNOS immunoreactivity in unstimulated cultures (E) and minimal response to KCl stimulation (F). These experiments were repeated in four different cultures in replicates of three wells per condition. Infection efficiency as monitored by GFP immunofluorescence varied between 50% and 95%. Shown are representative fields in which expression of GFP was >90%. (20× objective.)