Figure 5.
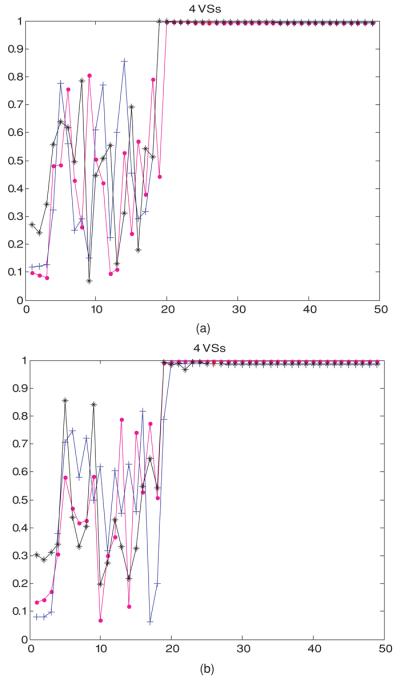
(a) Temperature-dependent perfusion: the dot product at each feedback iteration step between the heating vectors of model 3: the deviated pure-muscle initial model to the maximum eigenvector of model 1 (the standard linear model). The first heating vector was the minimum eigenvector of the approximate linear deviated pure-muscle reduced-order model constructed from four orthonormal virtual sources with constant perfusion, corresponding to the minimum (wtissue,1 in table 2, denoted by a magenta dot: •), average (wb in table 1, denoted by a blue cross: +) and maximum (wtissue,1 + wtissue,2 in table 2, denoted by a black star: ✩) values in figure 2. (b) Temperature-dependent perfusion: the dot product at each feedback iteration step between the heating vectors of model 4: the shifted-tumor-position initial model to the maximum eigenvector of model 1 (the standard linear model). The first heating vector was the minimum eigenvector of the approximate linear deviated pure-muscle reduced-order model constructed from four orthonormal virtual sources with constant perfusion, corresponding to the minimum (wtissue,1 in table 2, denoted by a magenta dot: •), average (wb in table 1, denoted by a blue cross: +) and maximum (wtissue,1 + wtissue,2 in table 2, denoted by a black star: ✩) values in figure 2.
