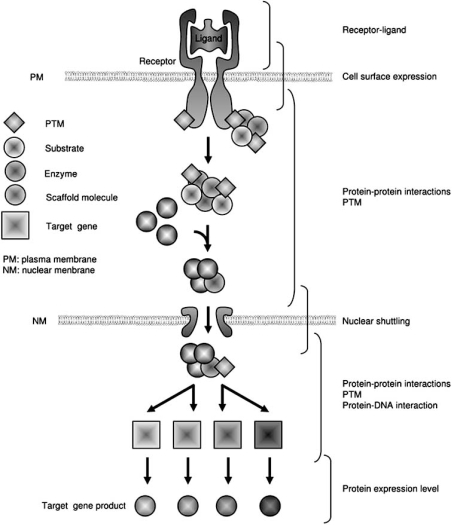
Fig. (3). Schematic representation of a canonical signaling pathway “from the plasma membrane to the nucleus”.
The receptor-ligand interaction occurring in the extracellular space leads to the activation of the membrane receptor which transduces a signal into the cytoplasm. At this stage, signaling can involve post-translational modifications of proteins (PTM), formation of complexes (scaffolds), modification of lipids and enzyme cascade activation (GTPases, kinases). Activated complexes can then translocate in the nucleus where transcriptional activation processes can take place, followed by mRNA maturation, expression and translation into active proteins.