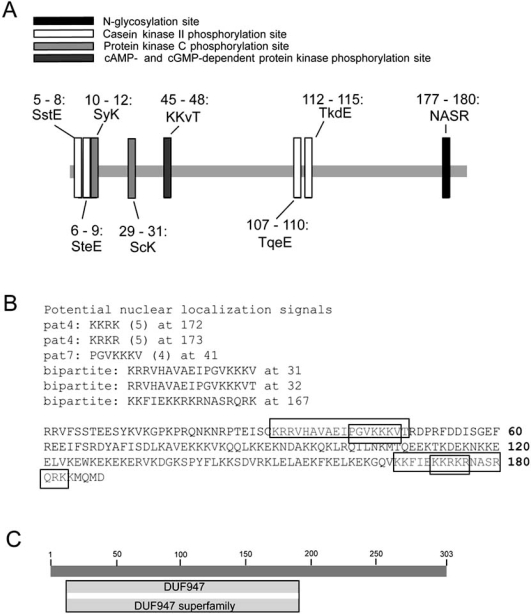
Fig. (3).
Identification of motifs and domains in SARP-3 protein. (A) Analysis of the primary sequence of SARP-3 identified a number of consensus sequences indicative of potential regions of post-translational modification. Putative sites included those for N-glycosylation, casein kinase II phosphorylation, protein kinase C phosphorylation, and cAMP-/cGMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylation. (B) A variety of potential nuclear localization sequences were identified within the 188 amino acids of the SARP-3 protein that were retrieved. Both ‘pat 4’ and ‘pat 7’ targeting motifs were identified (continuous basic residues) as well as bipartite motifs (two regions of basic amino acids separated by non-conserved residues). (C) SARP-3 contains a conserved region (DUF947), characteristic of a family of eukaryotic proteins with unknown function. This domain is described in InterPro, a database of protein families (domains, regions etc.) in which identifiable features found in known proteins can be applied to new protein sequences (see INTERPRO: IPR009292) and Pfam, a database of protein families represented by multiple sequence alignments and hidden Markov models (see PFAM: PF06102). Both entries have been identified across a range of phyla.