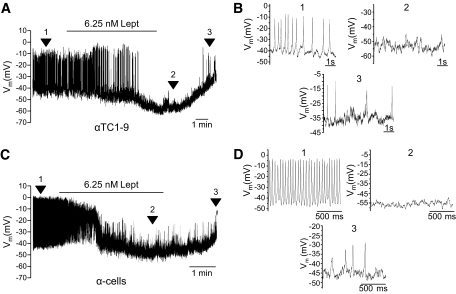
FIG. 2.
Leptin induces membrane hyperpolarization and inhibition of electrical activity. A: Recording of membrane potential in whole-cell configuration in αTC1-9 cells. With 0.5 mmol/l glucose, characteristic action potentials originated from a membrane potential of −39.9 ± 0.2 mV (n = 8). The application of leptin (6.25 nmol/l) induced hyperpolarization (21.1 ± 1.1 mV) and suppression of electrical activity. Removal of leptin allowed for a depolarization and recovery of electrical activity. Lept, leptin. B: Expanded records from A of different significant instants (indicated by numbers). C: With 0.5 mmol/l glucose, an intense electrical activity was recorded in mouse α-cells. Leptin (6.25 nmol/l) hyperpolarized these cells from −37.3 ± 0.6 mV to −60.6 ± 0.4 mV (n = 3) and decreased electrical activity. Lept, leptin. D: Expanded records from C of different significant instants (indicated by numbers).