FIG. 6.
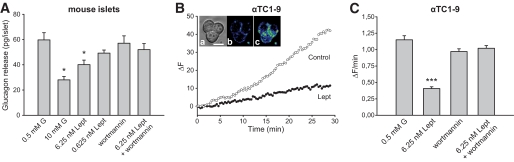
Effect of leptin on glucagon secretion. A: Glucagon secretion from mouse islets with 10 mmol/l glucose or with 0.5 mmol/l glucose plus 0.625 nmol/l or 6.25 nmol/l leptin was compared with the control (0.5 mmol/l glucose). The effect of wortmannin (50 nmol/l) on glucagon release with 0.5 mmol/l glucose in the absence and presence of 6.25 nmol/l leptin is also displayed. Data are shown as means ± SE (n = 8–13). B: Changes in FM1-43 fluorescence (ΔF; arbitrary units) versus time in αTC1-9 cells in control conditions (0.5 mmol/l glucose) and in the presence of leptin (6.25 nmol/l). Inset: images illustrating a group of cells in transmitted light (A) and loaded with FM1-43 at the beginning (B) and at the end of the record (C). Scale bar: 10 μm. C: The average rate of fluorescence changes as a function of time (ΔF/min) indicates that leptin reduces the exocytotic response. This effect was counteracted by wortmannin (20 nmol/l). Data are shown as means ± SE (n = 32–45 for each condition). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001 vs. control. G, glucose; Lept, leptin. (A high-quality representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)