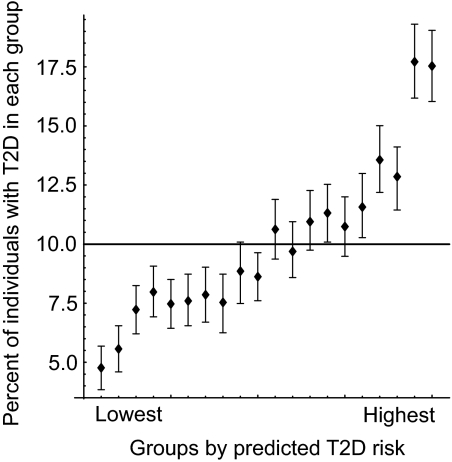
FIG. 4.
Estimation of the increase in type 2 diabetes risk from the combination of seven susceptibility variants previously identified and robustly replicated in the current study. We used case and control subjects with complete data from all stages of our study (n = 12,105). First, the risk for the genotypes of an SNP was estimated by logistic regression. Then, the multilocus risk for an individual was assessed as the sum of the risks for his/her genotype at seven SNPs. We simulated a population with 10% prevalence by bootstrap sampling. In the simulated population, we arranged the individuals in the order of their multilocus risk, sorted them into 20 equal-sized groups, and calculated the actual prevalence in each group. Means and 95% CIs of the groupwise prevalence were estimated based on 1,000 bootstrap sampling trials and are plotted in the figure. No significant gene-gene interaction was observed between the seven SNPs by multiple logistic regression analysis. T2D, type 2 diabetes.