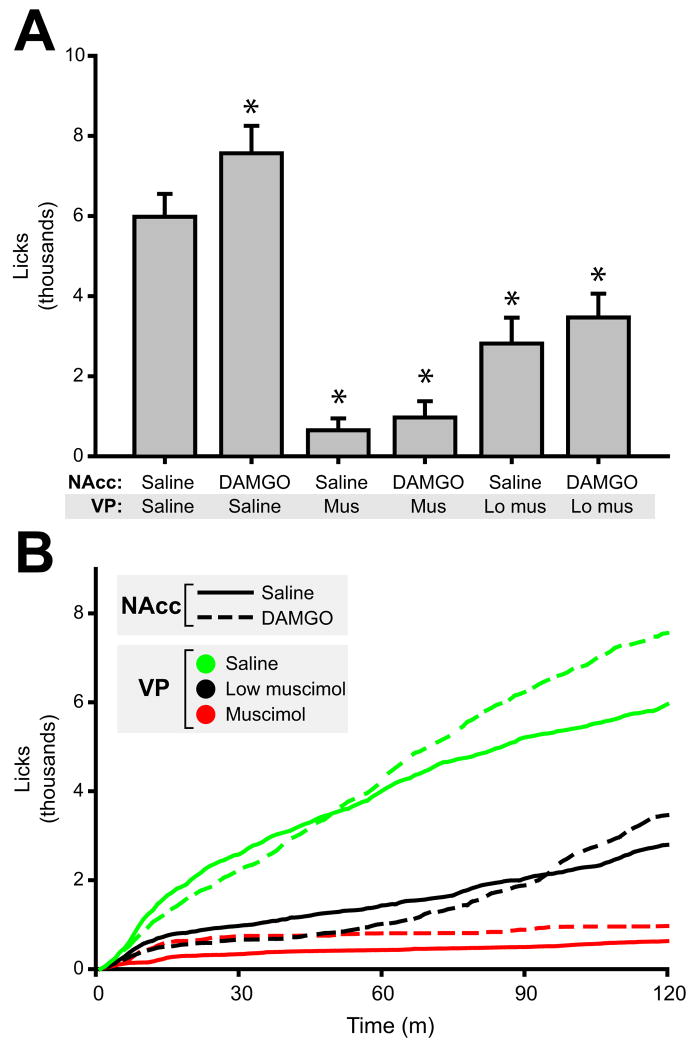
Figure 3.
NAcc DAMGO elevates sucrose consumption. (A) Stimulation of NAcc MORs increased mean (± SEM) 0.15 M sucrose consumption significantly. However, DAMGO effects were blocked with concurrent pharmacological inactivation of the VP. Both doses of muscimol infused into the VP had strong effects on baseline consumption of sucrose. NAcc DAMGO dose = 50 ng/μl; low VP muscimol dose = 25 ng/μl; high VP muscimol dose = 100 ng/μl. Asterisks indicated significant posthoc differences (P<0.05) from control (saline in NAcc and VP). (B) Time course of feeding. Solid lines indicate NAcc saline infusion; broken lines indicate NAcc DAMGO infusion. Colors indicate VP infusion: green = saline, black = low muscimol dose, red = high muscimol dose. Note that NAcc DAMGO (with VP saline infusion) caused a transient suppression of sucrose consumption (first ~45 minutes), followed by elevated rates of intake thereafter. N = 22 rats for data shown in Figures 3 – 7.