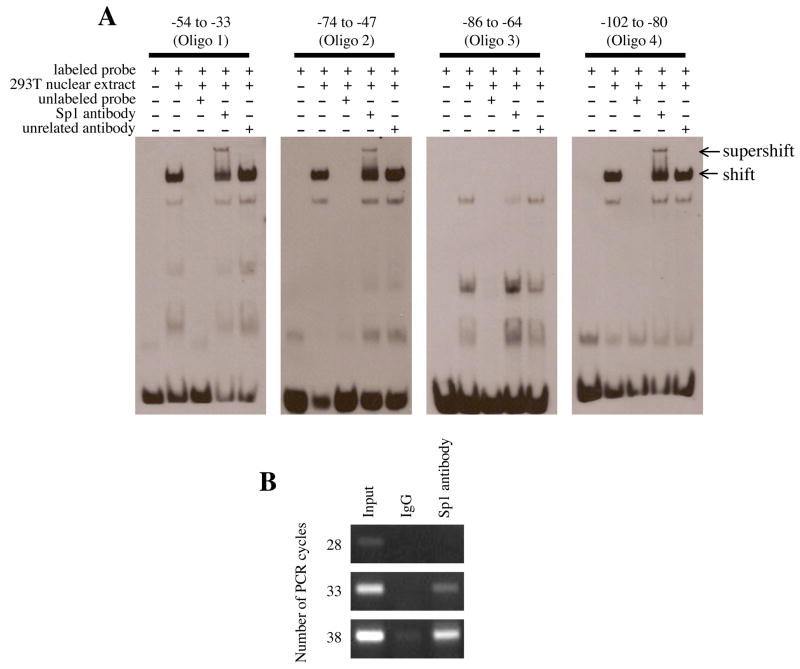
Figure 7.
EMSA and ChIP assay of the 5′-flanking region of EPHX2. (A) The electrophoretic mobility shift assay was performed using biotin-labeled probes (Oligo 1: −54 to −33, Oligo 2: −74 to −47, Oligo 3: −86 to −64, and Oligo 4: −102 to −80). Following incubation with nuclear extract and/or anti-Sp1 antibody, the reaction was separated by 6% native PAGE. A 100-fold molar excess of unlabeled probe was used in the competition assays. Arrows at the right indicate DNA-nuclear extract complex (shift) or DNA-nuclear extract- anti-Sp1 antibody complex (supershift). (B) The chromatin immunoprecipitation assay was performed using chromosomal DNA fragments (Input) from 293T cells. Immunoprecipitation was performed with control IgG or anti-Sp1 antibody. Following heat and proteinase K treatment, the released chromosomal DNA fragments were used as template for PCR using primers that specifically amplified the −214 to +28 region of the 5′-flanking region of EPHX2. The number of PCR cycles is shown to the left.