Figure 1.
Structure of the luciferase from Renilla reniformis
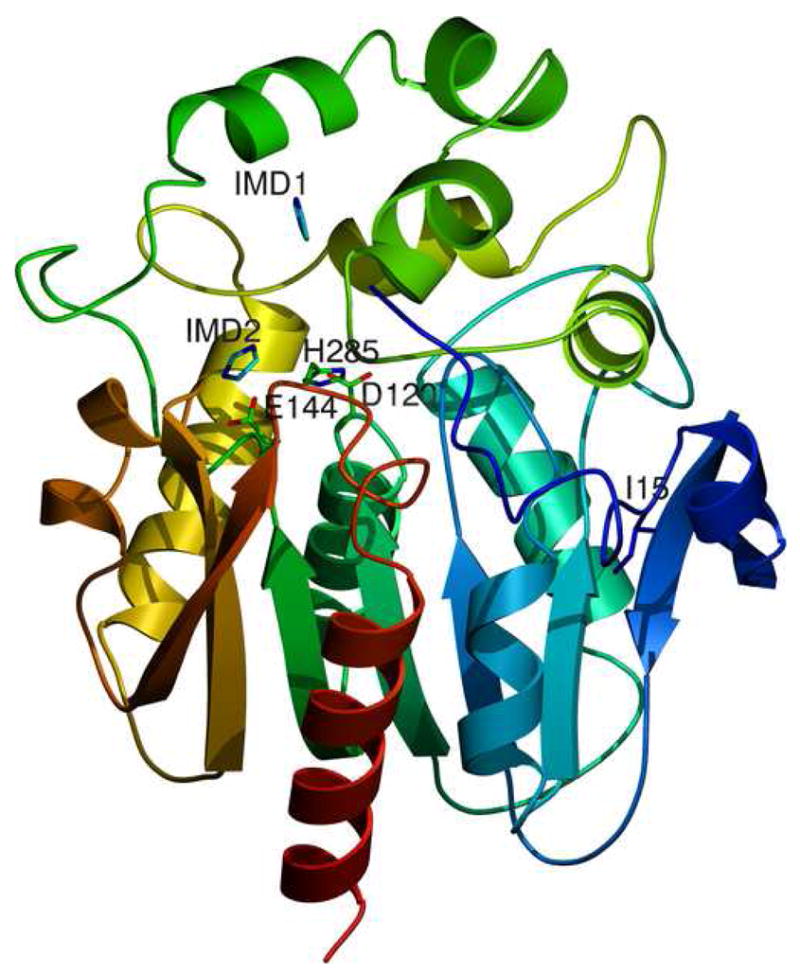
1a Cartoon representation of the structure derived from the RLuc8:diammonium condition. Residues 4–308 of RLuc8 are shown, with the N-terminus (N) in blue and the C-terminus (C) in red. The presumptive catalytic triad residues of D120, E144, and H285 [22] are marked, along with the two imidazole molecules (IMD1, IMD2) present in the structure. Also marked is the residue I15 mentioned in the discussion.
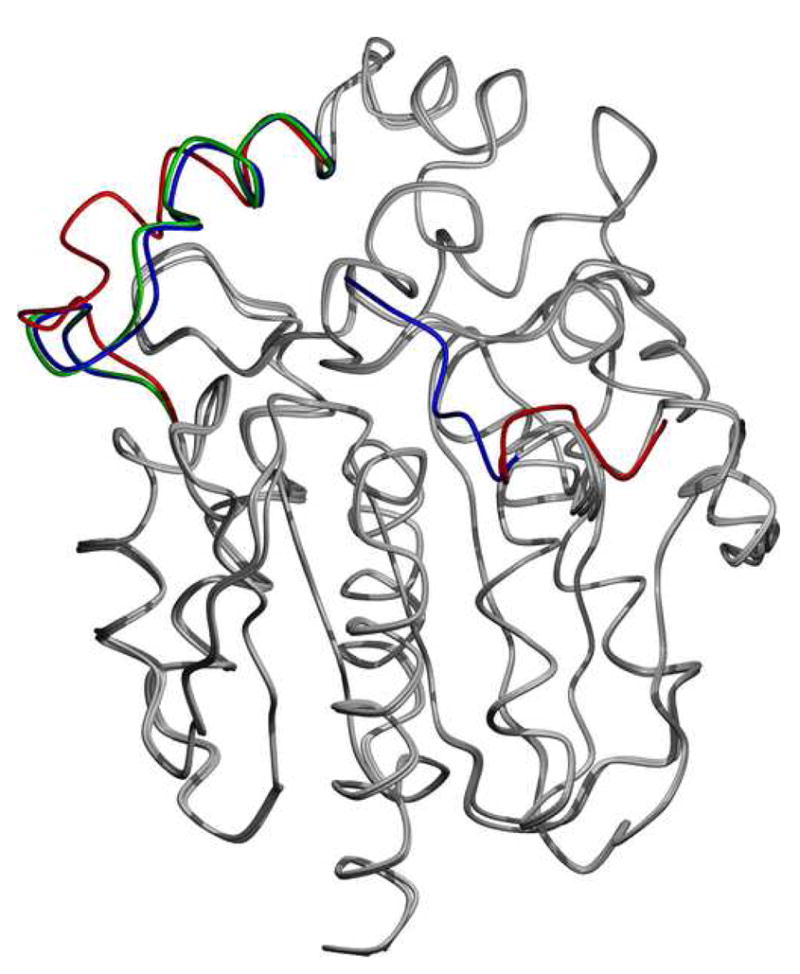
1b Superposition of the two monomers from the S3Rluc8:thiomaltoside condition and the diammonium structure. Regions that differ are the N-terminal domain and the loop domain over the active site. The regions of deviations are highlighted with blue for the diammonium condition, and red and green for monomers 1 and 2 of the thiomaltoside condition, respectively. Other than these two regions, the proteins are almost identical (Cα root mean square deviation <0.4 Å).
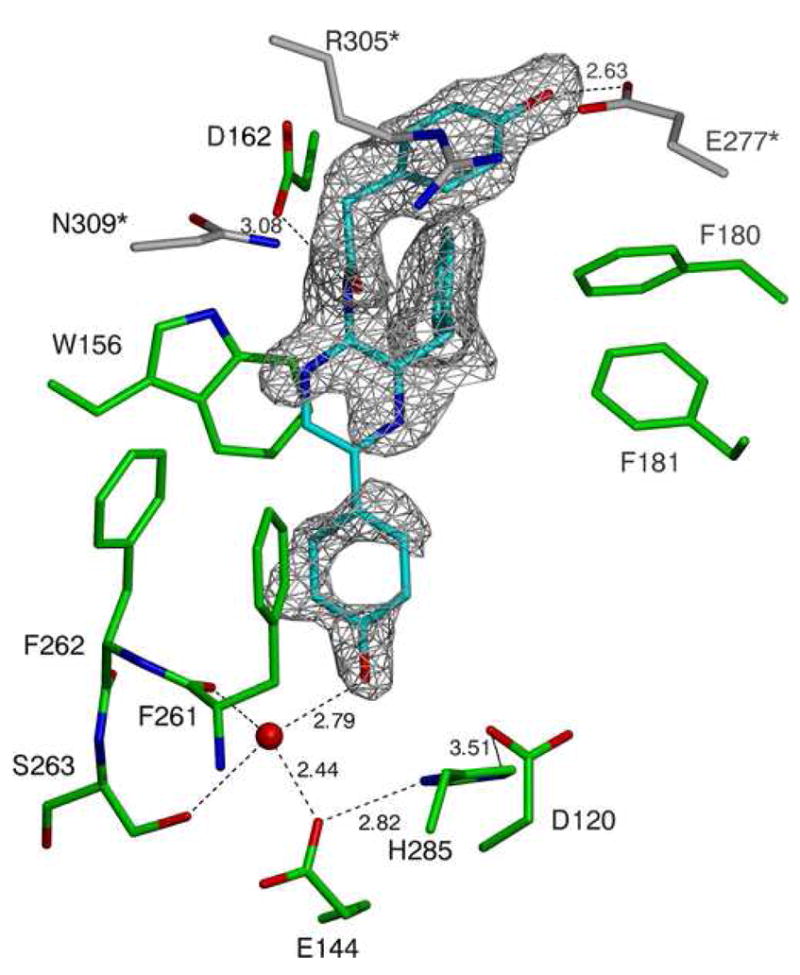
1c A close-up cartoon representation of the active site of the structure derived from the RLuc8:PEG/isopropanol condition. Coelenteramide is shown in cyan, residues from the luciferase molecule binding the coelenteramide are shown in green, and residues from the neighboring luciferase (via crystallographic contacts) are shown in gray. The red spheres represent water molecules, and the black dashed lines represent predicted hydrogen bonds. The gray mesh represents a σA weighted Fo - Fc difference map before the inclusion of the coelenteramide in the model phases, contoured at 2.0σ.
