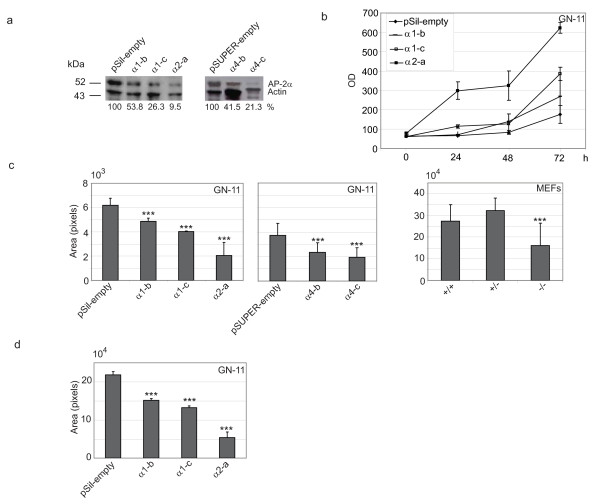
Figure 1.
AP-2α-dependent proliferation, migration and motility in GN-11 neurons and mouse embryo fibroblasts. (a) Stable GN-11 control clones named pSil-empty and pSUPER-empty or AP-2α-silenced clones named α1-a, α1-c, α2-a, α4-b and α4-c were analysed for their AP-2α protein levels by Western blot (WB). mAb 3B5 was used to detect AP-2α protein expression and actin expression was evaluated as protein loading control. The percentage values correspond to the amount of AP-2α protein present in each clone. (b) Proliferation was analysed in control pSil-empty or AP-2α-silenced α1-b, α1-c, α2-a GN-11 clones. Cells were plated and starved for 24 hours in serum-free medium, then 10% foetal calf serum (FCS) was added to cells. Cells were fixed and stained at the indicated time and optical density was measured. The experiments were performed in triplicate and repeated twice. (c) Migration was analysed in transwell assays for pSil-empty or pSUPER-empty or AP-2α-silenced α1-b, α1-c, α2-a, α4-b and α4-c GN-11 clones as well as for three independent preparations of AP-2α +/+, +/- and -/- mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEFs). Cells were plated in serum-free medium in the upper chamber and allowed to migrate over the medium containing 10% FCS for 18 hours. Each experiment was performed in triplicate and repeated twice. (d) pSil-empty or α1-b, α1-c, α2-a GN-11 clones were used to analyse motility in wound healing assays. Cells were grown at 90% confluency, serum starved for 24 hours, then a wound (cross) was made in the cell layer. 10% FCS medium was added and cells were allowed to migrate for 18 hours. Pictures of the right arm of the cross were taken at t = 0 hours and at t = 24 hours. Quantitations were performed as described in [24]. Differences were statistically significant as measured by a two-tailed Student's t-test (***, p < 0.05). (In (b), (c) and (d) the bars represent ± standard deviations.)