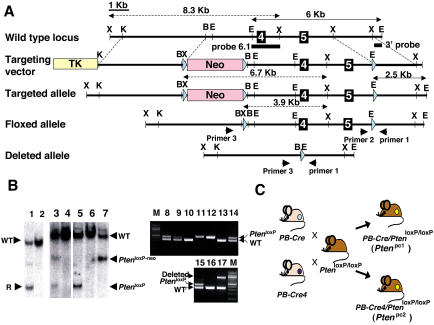
Figure 3. Conditional Knockout of the Pten Gene in Mouse Prostate.
(A) Map of wild-type Pten locus (top), targeting construct (second from top), predicted targeted locus (third from top), Pten locus after Cre-mediated excision of the Neo resistance cassette by crossing with an EIIA-Cre mouse (fourth from top), and Pten locus after Cre-mediated excision of the floxed exons 4 and 5 by crossing with a PB-Cre or PB-Cre4 transgenic mouse (bottom). The genomic sequence is depicted as a black line, with black boxes representing exons 4 and 5. Pink and yellow boxes represent the Neo resistance and the HSV thymidine kinase cassette (TK) and light blue triangles represent the loxP site, respectively. The Pten genomic fragments used as a probe for Southern blot analysis are shown (3′ probe and probe 6.1). Solid arrows represent expected fragments following hybridization with the 3′ probe upon digestion with EcoRI, and dashed arrows represent expected fragments following hybridization with the probe 6.1 upon digestion with XbaI. Locations of PCR primers to detect wild-type, floxed allele (PtenloxP), and deleted allele are shown. XbaI (X), KpnI (K), BamHI (B), and EcoRI (E) sites are shown.
(B) Genotyping of mice. Lanes 1 and 2 show Southern blot analysis of ES cell clones with 3′ probe of control (lanes 2) and recombined clones and #176 (lane 1) after digestion with EcoRI, showing a 6 kb wild-type band (WT) and a 2.5 kb targeted band (R). Lanes 3 and 4 (control) represent Southern blot analysis of mouse tail DNA of offspring by crossing F1 mouse generated from #176 with an EIIA-Cre mouse with probe 6.1 after digestion with XbaI, showing wild-type, targeted (PtenloxP-neo), and floxed (PtenloxP) locus bands. Lanes 5, 6 (control), and 7 represent Southern blot analysis of mouse tail DNA of offspring by crossing the mouse of lane 3 with a wild-type mouse with probe 6.1 after digestion with XbaI. Lanes 8–14 show PCR analysis of tail DNA of offspring by crossing a PB-Cre4 (+), PtenloxP/+ male with a PtenloxP/+ female with primers 1 and 2. Lanes 8, 9, and 14 indicate PtenloxP/+ , lanes 10 and 13 indicate Pten+/+,and lanes 11 and 12 indicate PtenloxP/loxP. Lanes 15–17 show PCR analysis of tail DNA of offspring by crossing a Ptenloxp/+ male with a PB-Cre4(+), PtenloxP/+ female with primers 1, 2, and 3. Lane 15 indicates PtenloxP/+, lane 16 indicates Pten+/+, and lane 17 indicates that the deleted allele exists in tail DNA of this offspring.
(C) Representation of crossing scheme used to generate prostate-specific Pten conditional mutants. PtenloxP/loxP mutants were crossed with PB-Cre transgenic mice or PB-Cre4 transgenic mice.