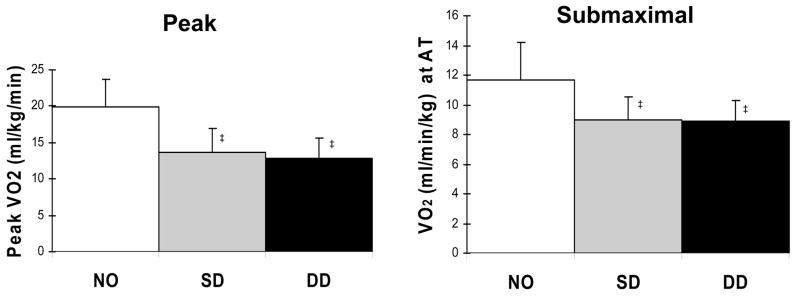
Figure 2.
Exercise oxygen consumption (VO2) during peak exhaustive exercise (left panel) and during submaximal exercise at the ventilatory anaerobic threshold (right panel) in age matched normal subjects (NO), elderly patients with heart failure due to systolic dysfunction (SD), and elderly patients with heart failure with normal systolic function, presumed diastolic dysfunction (DD). Exercise capacity is severely reduced in patients with diastolic heart failure compared to normals (p<0.001) and to a similar degree as in those with systolic heart failure. Overall, peak exercise VO2 was 33% lower in the women compared to the men (not shown). Data from Kitzman DW, Little WC, Brubaker PH, Anderson RT, Hundley WG, Marburger CT et al. Pathophysiological characterization of isolated diastolic heart failure in comparison to systolic heart failure. JAMA 2002; 288(17):2144–2150.