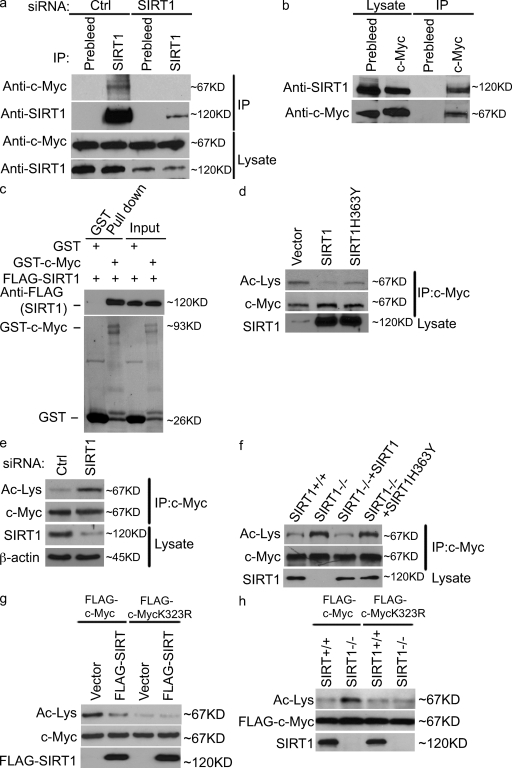
Figure 2.
SIRT1 interacts with c-Myc and deacetylates c-Myc at K323. (a and b). HeLa cells were transfected with control (ctrl) or SIRT1 siRNA (a) or left untransfected (b). Cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (c) Purified Flag-SIRT1 was incubated with recombinant GST or GST–c-Myc coupled to glutathione-Sepharose. Proteins retained on the beads were blotted with the indicated antibodies. (d) The indicated constructs were transfected into 293T cells. 48 h later, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (e) Cells were transfected with control or SIRT1 siRNA. 72 h later, the acetylation (Ac) level of c-Myc was detected as in d. (f) SIRT1+/+, SIRT1−/−, and SIRT1−/− reconstituted with SIRT1 and SIRT1-H363Y were lysed, and the acetylation level of c-Myc were detected as in d. (g) The indicated constructs were transfected into cells. 48 h later, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (h) SIRT1+/+ and SIRT1−/− cells were transfected with the indicated expressing constructs. 48 h later, cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. To compare the acetylation of c-Myc, the levels of c-Myc were equalized in d–h.