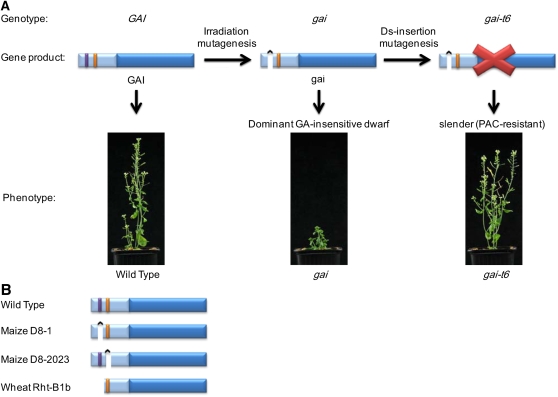
Figure 2.
Wild-Type and Mutant DELLAs.
(A) The Arabidopsis mutant gai allele confers dominant GA-insensitive dwarfism and was derived from the wild-type allele (GAI) via irradiation mutagenesis (see Koornneef et al., 1985; Peng et al., 1997). gai encodes a mutant gai protein that lacks the DELLA domain (purple section in the GAI protein). It is the lack of the DELLA domain that causes the altered function of gai, making it a constitutive growth inhibitor whose activity is not opposed by GA. Subsequent Ds insertion mutagenesis experiments yielded the gai-t6 allele. This knockout allele does not encode a functional GAI (or gai) protein and confers a tall, slender (PAC-resistant) phenotype.
(B) The mutant maize D8-1, D8-2023, and wheat Rht-B1b proteins confer dominant GA-insensitive dwarfism. The maize and wheat genomes encode DELLA proteins (d8 and Rht-B1a, respectively). Maize mutant alleles encode mutant D8-1 (lacks the DELLA domain, domain I, in purple), mutant D8-2023 (lacks the TVHYNPS domain, domain II, in orange), and wheat mutant Rht-B1b lacks domain I (see also Peng et al., 1999a).