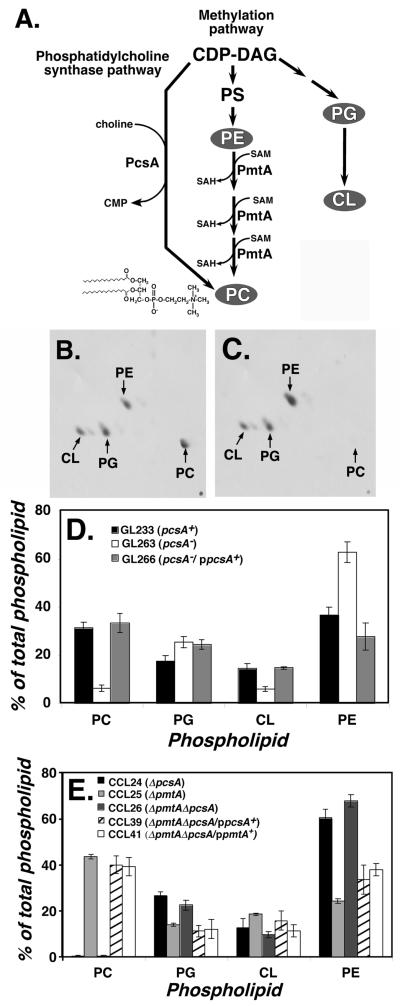
Figure 1. Knockout of pcsA causes drastic loss of PC content in L. pneumophila membranes.
(A). Pathways for phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis in bacteria. Shown are the two major pathways for synthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC) in bacteria, catalyzed by phosphatidylcholine synthase (PcsA) and phospholipid N-methyltransferase (PmtA). L. pneumophila Philadelphia 1 ORFs encoding both of these enzymes have the predicted activities when expressed in E. coli (Martinez-Morales et al., 2003). CDP-DAG: cytidine diphospho-diacylglyceride. PS: phosphatidylserine. PG: phosphatidylglycerol. CL: cardiolipin. SAM: S-adenosylmethionine. SAH: S-adenosylhomoserine. PE: phosphatidylethanolamine. In gray are the three major lipids found in bacterial membranes in addition to PC (Lopez-Lara and Geiger, 2001). (B). Phospholipid content of L. pneumophila labeled with [1-14C]acetate was determined by thin layer chromatography (TLC) of membrane extracts (Experimental Procedures). Shown is two-dimensional TLC fractionation of GL233 (pcsA+) lipids. (C). Phospholipids from GL263 (pcsA−) prepared as above and subjected to two-dimensional TLC fractionation. (D). Complementation of PC biosynthesis defect by cloned pcsA+ gene. Displayed are relative percentages of phospholipids in various L. pneumophila strains having either an intact pcsA+ gene or the pcsA− mutation. Data shown are mean of triplicate samples. (E). Total absence of PC in ΔpcsA ΔpmtA strain and its complementation. Phospholipid profiles are displayed as in (D) for strains noted in legend. Data shown are mean of triplicate samples. PC: phosphatidylcholine. PE: phosphatidylethanolamine. PG: phosphatidylglycerol. CL: cardiolipin.